
Managing AWS access and permissions can seem overwhelming, especially when you need to give team members access to billing information. Without proper setup, you risk exposing sensitive financial data or accidentally granting excessive permissions.
The good news? Creating secure IAM users with appropriate billing access is straightforward when you follow the right steps.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn how to create IAM users safely, configure billing permissions correctly, and implement security best practices that protect your AWS environment. Whether you’re a startup founder needing to give your CFO billing access or an enterprise administrator managing multiple team members, this tutorial has you covered.
By the end of this article, you’ll have the knowledge and confidence to manage IAM users like a pro while keeping your AWS account secure.
What is AWS IAM?
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a comprehensive security service that enables you to control who can access your AWS resources and what actions they can perform.
Think of IAM as the digital gatekeeper for your AWS environment. It ensures only authorized users and applications can access specific resources with the exact permissions they need.
In 2025, IAM has become more critical than ever. Organizations face increasing cybersecurity threats and compliance requirements.
Modern IAM implementations focus heavily on the principle of least privilege and zero-trust security models. By default, IAM users don’t have access to the AWS Billing and Cost Management console, and users and roles don’t have permission to create or modify Billing resources without explicit IAM policies.
Now that you understand what IAM is, let’s explore why creating dedicated IAM users is crucial for your AWS account security.
Why Create IAM Users for Your AWS Account
Proper IAM user management is essential for several reasons:
- Security: Prevents unauthorized access to your AWS resources and sensitive data.
- Cost Control: Restricts who can create or modify billable resources.
- Compliance: Meets regulatory requirements for access control and audit trails.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlines user onboarding and offboarding processes.
- Risk Mitigation: Reduces the impact of potential security breaches.
Understanding these benefits highlights why proper IAM setup is essential. Before diving into the creation process, let’s ensure you have everything needed to get started.
Prerequisites for Creating IAM Users
Before creating IAM users, ensure you have:
- AWS root account access (use sparingly for security)
- Understanding of your organization’s access requirements
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) device ready
- Clear role definitions for different user types
- Access to AWS Management Console
- Knowledge of required IAM policies for your use case
⚠️ Security Note: AWS strongly recommends using federated access with temporary credentials instead of long-term IAM users for human access in 2025.
This approach provides better security and easier management.
How to Create IAM Users Step-by-Step
Follow this comprehensive guide to create secure IAM users with proper permissions and access controls.
Step 1: Access the IAM Console
1. Sign in to AWS Console
- Navigate to https://aws.amazon.com
- Sign in with your AWS account root user (only when necessary)
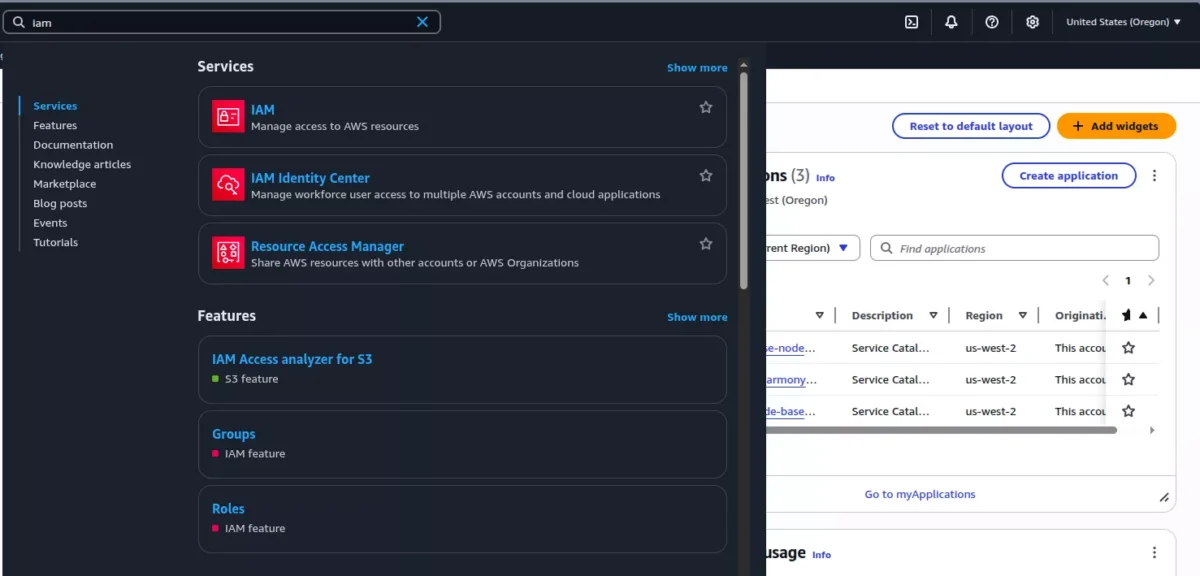
2. Open IAM Service
- In the AWS Console search bar, type “IAM”
- Select “IAM” from the dropdown results
- You’ll be directed to the IAM dashboard
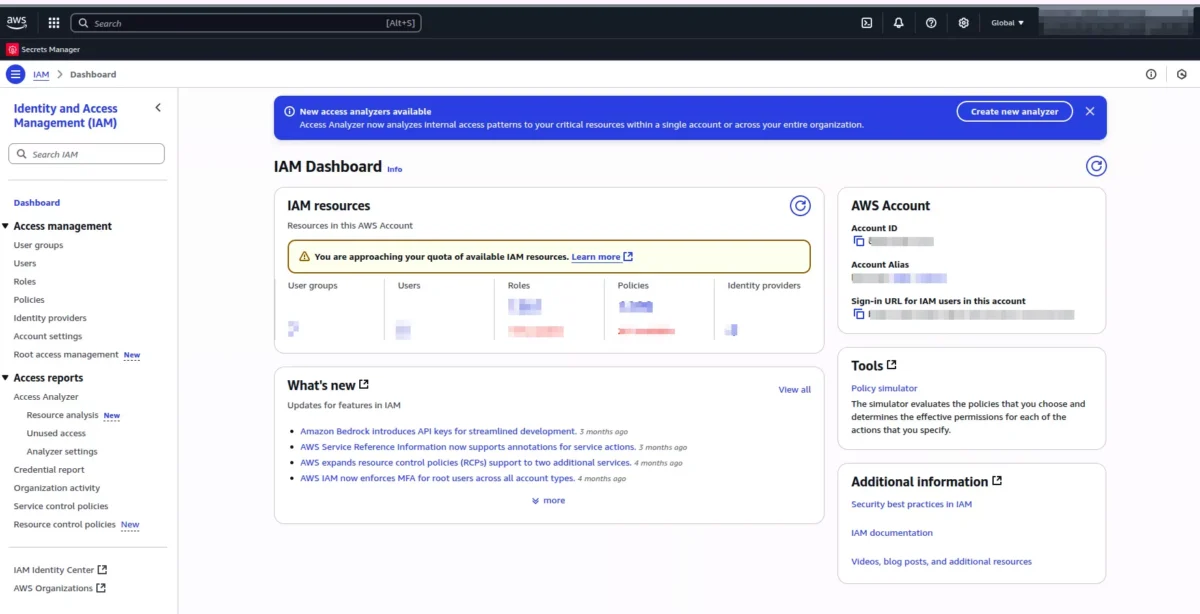
Step 2: Configure Account Settings
Before creating users, configure your account-wide IAM settings:
1. Customize Sign-in Link (Optional)
- Click “Dashboard” in the left navigation
- Under “AWS Account,” click “Customize” next to the sign-in URL
- Enter a memorable account alias
- Click “Save changes”
Step 3: Create Your First IAM User
1. Navigate to Users
- Click “Users” in the left navigation pane
- Click “Create user”
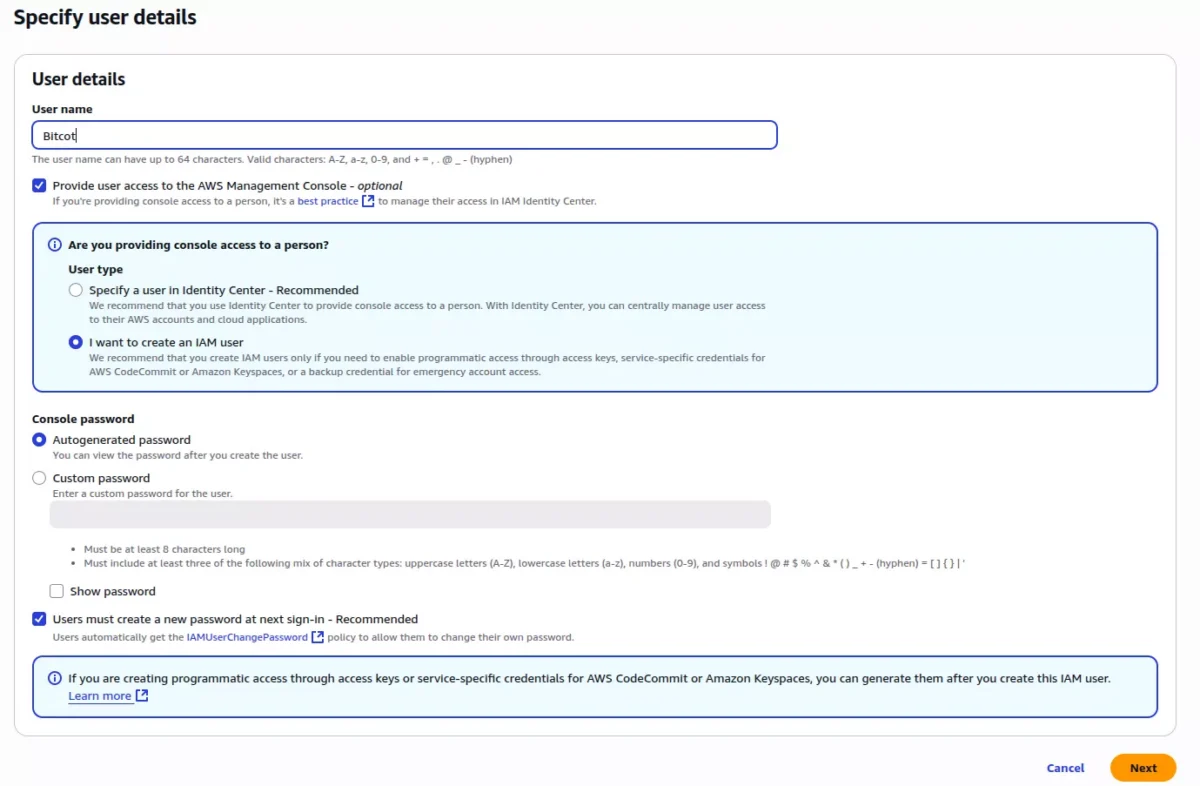
2. Set User Details
- User name: Enter a descriptive username (e.g., john.doe or billing-admin)
- Console access: Check if the user needs AWS Console access
- Console password: Choose between auto-generated or custom password
- Require password reset: Recommended for security
3. Configure Permissions
- Select “Attach policies directly” for granular control
- For billing access, search and select “Billing” or “AWSBillingReadOnlyAccess” policy
- Avoid using AdministratorAccess unless absolutely necessary
4. Add Tags (Optional but Recommended)
Add meaningful tags like:
- Department: Finance
- Role: BillingManager
- Environment: Production
5. Review and Create
- Review all settings carefully
- Click “Create user”
Step 4: Secure the User Account
After creation, immediately:
1. Download Credentials
- Download the .csv file containing login credentials
- Store it securely (password manager recommended)
- Delete the file from downloads after secure storage
2. Set Up MFA
- Go to the user’s security credentials tab
- Click “Assign MFA device”
- Choose between virtual MFA, hardware token, or SMS
You’ve successfully created your IAM user! However, if you need billing access, there’s a crucial additional configuration step we need to cover next.
How to Give IAM Users Billing Access
Learn how to configure billing permissions safely while maintaining security best practices.
Enabling IAM Access to Billing
- Assign Billing Permissions Choose the appropriate billing policy:
- AWSBillingReadOnlyAccess: View-only billing information
- Billing: Full billing access including payment methods
- AWSAccountManagementFullAccess: Complete account management
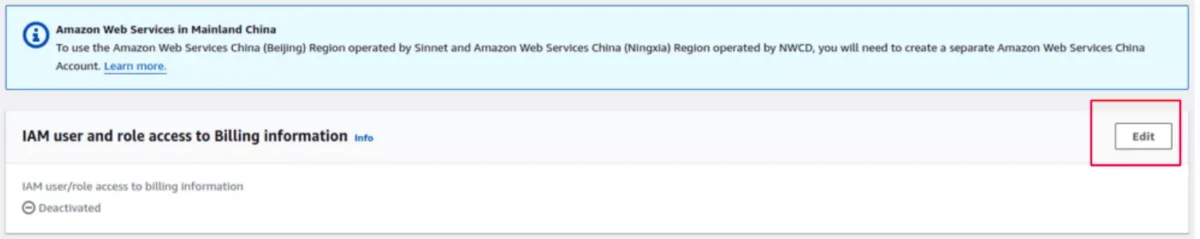
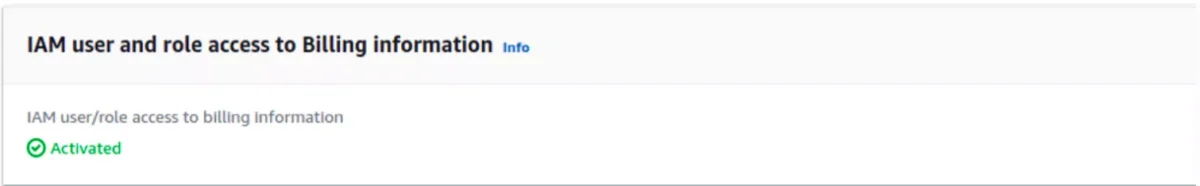
Important: The AWS account root user must first activate IAM access before any IAM users can access the Billing and Cost Management console.
This is required even with proper IAM policies attached.
2. Assign Billing Permissions Choose the appropriate billing policy:
- AWSBillingReadOnlyAccess: View-only billing information
- Billing: Full billing access including payment methods
- AWSAccountManagementFullAccess: Complete account management
Custom Billing Policy Example
For enhanced security, create a custom policy with specific permissions:
This gives you granular control over what billing information users can access.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"aws-portal:ViewBilling",
"aws-portal:ViewUsage",
"aws-portal:ViewAccount"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Now that your users have the necessary billing access, it’s essential to implement proper security measures to protect your AWS environment.
AWS IAM Security Best Practices
Implement these essential security measures to protect your AWS environment and user accounts.
1. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA is essential for all IAM users, especially those with billing access. Configure MFA immediately after user creation. This adds an extra layer of security beyond just passwords.
2. Apply Principle of Least Privilege
Grant users only the permissions they need to perform their job duties. Regularly review and adjust permissions as roles change.
3. Use Temporary Credentials When Possible
AWS recommends using federation with identity providers for human users. This provides temporary credentials rather than long-term access keys. It’s more secure and easier to manage.
4. Regular Access Reviews
- Conduct quarterly access reviews
- Remove unused IAM users promptly
- Monitor AWS CloudTrail logs for suspicious activity
- Review and audit IAM policies regularly
5. Strong Password Policies
- Minimum 14 characters
- Complex character requirements
- Regular password rotation
- No password reuse
6. Avoid Root Account Usage
Only use the AWS account root user for tasks that specifically require it. For daily operations, always use IAM users or IAM roles with appropriate permissions.
Common IAM User Creation Mistakes to Avoid
Prevent these frequent security and configuration errors that could compromise your AWS account.
1. Overusing AdministratorAccess
Many organizations default to giving users full administrative access. This violates the principle of least privilege and creates unnecessary security risks. Only grant admin access when absolutely required.
2. Sharing IAM User Credentials
Never share IAM user credentials between team members. Create individual users for each person requiring access. This ensures proper accountability and security.
3. Neglecting MFA Setup
Failing to implement MFA significantly increases security risks. This is especially dangerous for users with billing or administrative access. Always set up MFA immediately after creating accounts.
4. Ignoring Access Key Management
Long-term access keys should be rotated regularly and removed when no longer needed. Unused access keys are a major security vulnerability.
5. Insufficient Monitoring
Not monitoring IAM user activity through CloudTrail can lead to undetected security incidents. Set up proper logging and alerts for suspicious activities.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you’ll have a much more secure IAM setup. If you run into any issues along the way, here are some frequently asked questions that might help.
Conclusion
Creating IAM users with proper billing access is a fundamental aspect of AWS security management. By following the best practices outlined in this guide, you’ll establish a secure foundation for your AWS environment while maintaining operational efficiency.
Remember that IAM is not a one-time setup. It requires ongoing management, monitoring, and optimization. Regular reviews of user permissions, implementation of the latest security features, and adherence to the principle of least privilege will help protect your AWS resources and data.
For more complex scenarios or enterprise-scale implementations, consider consulting with AWS security experts or certified partners. This ensures your IAM configuration meets your specific organizational needs and compliance requirements.
Need Help? If you’re implementing IAM for a complex organization or need assistance with advanced security configurations, consider reaching out to AWS Professional Services or certified AWS partners for expert guidance.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many IAM users can I create?
AWS allows up to 5,000 IAM users per AWS account by default. Contact AWS Support for limit increases.
Should I use IAM users or federated access?
AWS recommends federated access with temporary credentials for human users. Use IAM users primarily for service accounts and when federation isn’t feasible.
How often should I rotate access keys?
AWS recommends rotating access keys every 90 days. Consider shorter rotation periods for high-privilege accounts.
Can I recover deleted IAM users?
No, deleted IAM users cannot be recovered. Ensure you have proper backup procedures and approval processes for user deletion.
What's the difference between IAM users and root users?
The root user has complete access to all AWS services and resources. IAM users have permissions only as explicitly granted through policies.












