
Your next million-dollar decision doesn’t happen in a boardroom – it happens when you choose your tech stack.
And here’s what nobody tells you about that decision…
66% of technology initiatives exceed budgets by 27%. Mid-scale projects now cost 30-40% more than three years ago. The wrong tech stack forces costly rewrites that set you back 6-18 months.
But the real cost isn’t in the budget spreadsheet.
The wrong stack costs you time to market. It forces you to compete with one hand tied behind your back. Technical debt compounds monthly while competitors ship faster.
84% of developers now use AI-powered development tools, with 51% using them daily. Global IT spending is projected to reach $6.08 trillion in 2026, with software spending alone growing 15.2%. AI infrastructure software spending is expected to hit $230 billion in 2026, fundamentally reshaping what “the right stack” means.
What makes this guide different? Unlike generic tech stack articles that list technologies without context, this guide gives you a proven decision framework used by 200+ companies – from funded startups to enterprise leaders managing seven-figure budgets.
You’ll discover the exact evaluation criteria that separate successful projects from failed ones, hidden costs that don’t appear in estimates, and red flags that signal expensive mistakes.
But before we dive into the selection framework, let’s establish a foundation. You can’t choose the right tech stack if you don’t fully understand what one is and why it matters so much.
What Is a Tech Stack and Why Does It Matter
A tech stack represents the complete collection of programming languages, frameworks, libraries, databases, and tools used to build and run your software application.
Think of it as the foundation and engine of your digital product – from what users see to how your app scales under load.
But here’s what most people miss…
It’s an interconnected ecosystem where each component affects the others. Make one wrong choice, and it creates a domino effect.
Your frontend framework choice influences state management complexity. Your database selection impacts query performance and costs. Your hosting infrastructure determines deployment speed.
Every decision is connected. Every choice has consequences.
The Core Components Explained
Every tech stack consists of distinct layers. If your budget allows for $20,000 or more, you can consider building a complete stack with the following core components.
Frontend (client-side): Handles what users see – React, Angular, Vue.js, HTML, CSS, JavaScript
Backend (server-side): Powers business logic and data processing – Node.js, Python (Django, Flask), Java (Spring Boot), Ruby on Rails
Database: Stores application data – PostgreSQL, MySQL (relational) or MongoDB (NoSQL)
Infrastructure: Cloud hosting and DevOps – AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, Docker, Kubernetes
Real-world example: Airbnb’s tech stack includes React (frontend for fast, interactive UI), Ruby on Rails (backend for business logic), PostgreSQL (database for structured booking data), and AWS (infrastructure for global scaling). Each layer serves a specific purpose, but changing one affects the others. When they switched from monolithic Rails to microservices, it required frontend changes, database partitioning, and new infrastructure – a $50M+ investment.
Why Your Tech Stack Choice Matters More Than Ever
The wrong tech stack slows development by 30-50%, inflates cloud costs by 200-300%, and creates hiring bottlenecks. Most critically, it makes scaling prohibitively expensive without a complete rebuild.
But let’s talk real numbers…
Software development costs range from $40,000-$80,000 for MVPs, $100,000-$250,000 for mid-range apps, and $200,000-$500,000+ for enterprise systems.
Here’s what this means: choosing MongoDB over PostgreSQL might save $20,000 initially but cost $50,000 more annually. Picking microservices too early doubles infrastructure complexity and extends timelines by 4-6 months. Selecting a rare framework reduces your hiring pool by 80%.
With AI integration adding 20-30% to costs, serverless architectures changing cost models, and edge computing affecting global performance, every decision creates compounding implications.
Quick Reality Check:
- Can we hire developers for this stack within 60 days?
- Will this handle 10x growth without major refactoring?
- Do we understand the total 3-year cost?
If you answered “no” to any question, pause and reconsider.
This is why we created a systematic approach – one that removes emotion and guesswork.
Understanding Different Types of Tech Stacks

Not all tech stacks are created equal. And that’s actually good news.
The best tech stack for a mobile app differs dramatically from enterprise SaaS. Understanding these distinctions helps you match technology to your use case – and avoid copying what works for someone else.
Web Application Stacks
Web apps offer the most cost-effective starting point. Single codebase works across all devices and browsers, reducing development time and maintenance.
Popular stacks: MERN (MongoDB, Express, React, Node.js) for JavaScript teams, Python (Django/Flask) with PostgreSQL.
Best for: SaaS platforms, content management systems, eCommerce, business tools, admin dashboards, B2B applications.
Start with web when:
- Your users primarily work on desktops/laptops
- You don’t need device-specific features (camera, GPS, push notifications)
- You want to validate product-market fit quickly and cheaply
- Your target users expect to access via browser (business software, data tools)
Consider mobile when: Device features are core to experience, users primarily engage on phones, or offline access is critical.
Mobile Application Stacks
Native development (Swift for iOS, Kotlin for Android): Superior performance, full device access, but requires separate codebases.
Cross-platform (React Native, Flutter): Write once, deploy to both platforms. 30-40% cost savings with near-native performance.
Cost Reality:
- Native iOS + Android: $120K-$300K (8-12 months)
- Cross-platform: $80K-$200K (5-8 months)
Choose native for gaming, AR/VR, or cutting-edge features. Choose cross-platform for faster time-to-market and budget constraints.
Enterprise Software Stacks
Prioritize stability, security, and compliance. Common combinations: Angular/React + Java (Spring Boot) or .NET Core + enterprise databases (Oracle, SQL Server).
When to choose enterprise stacks:
- You’re building for Fortune 500 or heavily regulated industries
- System will be maintained for 10+ years
- Integration with existing enterprise systems (SAP, Salesforce, Oracle) is critical
- Compliance requirements (SOC 2, ISO 27001) demand established frameworks
- You need vendors you can call for 24/7 support
Key differences from startup stacks:
- Slower initial development but fewer surprises at scale
- Higher upfront costs but predictable long-term expenses
- Extensive tooling for monitoring, deployment, governance
- Talent pools in enterprise hubs (not startups)
Costs start at $200K, often exceed $500K, but deliver ROI within 18-36 months through operational efficiency, reduced downtime, and compliance peace of mind.
Data-Driven and AI Stacks
Leading AI stack: Python + FastAPI + LangChain + vector databases (Pinecone, Weaviate). Learn more about our AI development services.
Build AI features quickly, experiment with low risk, integrate NLP and automation smoothly. However, AI adds 20-30% to costs through API fees and GPU infrastructure.
Serverless and Cloud-Native Stacks
Serverless (AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions) eliminates infrastructure management. Pay only for compute time used, scale automatically, eliminate server overhead.
Ideal for: MVPs, event-driven apps, variable traffic patterns.
But here’s the thing…
Knowing all these stack types doesn’t solve your problem. You’re still left wondering which one fits YOUR situation.
Now that you understand the different categories of tech stacks, the natural question becomes: How do you actually choose between them?
That’s where most teams struggle. They understand the options but lack a systematic way to evaluate which option fits their specific situation. Let’s fix that.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Your Tech Stack
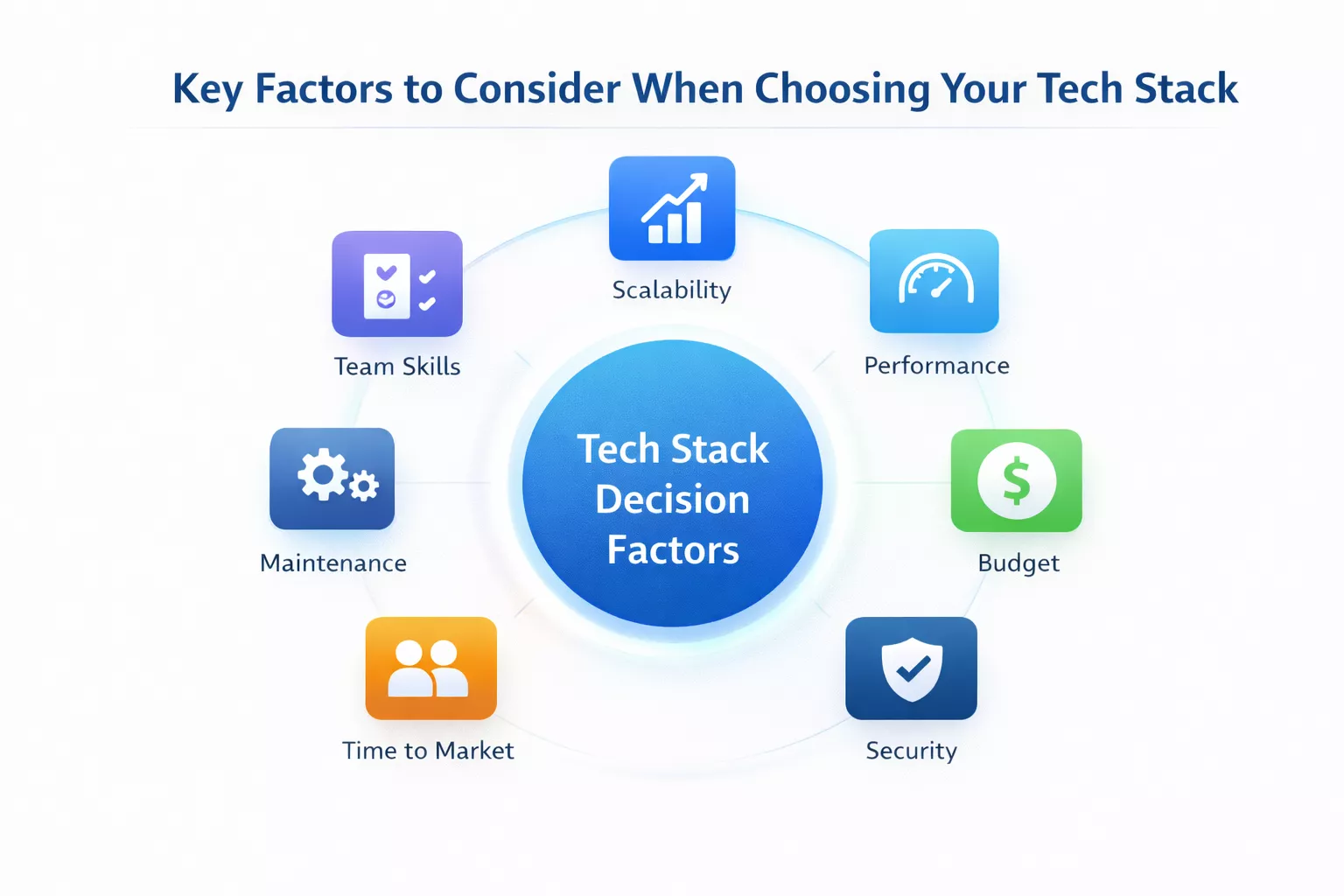
Here’s where most tech stack decisions go wrong…
Founders fall in love with technologies. CTOs optimize for the wrong metrics. Teams chase trends instead of outcomes.
Successful selection requires balancing competing priorities. Let’s break down the decision framework that actually works.
Project Requirements and Goals
Start with clarity about what you’re building. Define your core business objectives – cost reduction? New revenue? Better UX? Market expansion?
Identify target users and devices. Consumer apps need mobile-first design. B2B tools focus on desktop browsers. Global audiences require multi-language support.
Prioritize features:
- Must-Have: Without these, product provides no value
- Important: Enhance value significantly
- Nice-to-Have: Marginal improvements
Non-functional requirements with numbers:
- Expected traffic (concurrent users, requests/second)
- Required uptime (99.9% = 8.7 hours downtime/year)
- Response times (API calls, page loads)
- Compliance (GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, PCI DSS)
Scalability and Performance Needs
Think beyond current users. Can your stack handle 10x growth without complete rewrite?
Here’s why this matters: A healthcare startup we worked with launched with 500 users. Within 18 months, they hit 50,000. Because they chose a scalable stack initially, they handled 100x growth with minor optimizations. A competitor using an inflexible stack spent $200,000 rebuilding.
Horizontal scaling (adding servers) works better than vertical (upgrading existing). Microservices scale components independently but add complexity. Well-designed monoliths often serve startups better initially.
Database choices create long-term implications: PostgreSQL offers strong consistency and powerful querying – ideal for financial data or complex relationships. However, it costs more to scale vertically. MongoDB scales horizontally easier and handles unstructured data well, but requires careful schema design to avoid performance issues later.
Which should you choose? If your data has clear relationships (users, orders, products), go relational. If you’re storing varied document types (content, logs, events), consider NoSQL.
Development Team Skills and Expertise
The most appropriate tech stack is the one your team can deliver today. List actual skills – JavaScript, .NET, Java, Python.
Adopting new technologies extends projects by 30-50%. Training costs money. Mistakes create technical debt.
Balance team comfort with evolution. For MVPs, favor team strengths. Introduce new technologies as product proves market fit.
Talent Availability and Hiring Considerations
Check developer availability in your region before finalizing. Rare tech stacks increase hiring costs and slow velocity.
JavaScript developers: 16.5 million globally. Python shows AI/ML-driven growth. React developers outnumber Angular developers, affecting hiring speed and salaries.
Consider location and remote work. SF Bay Area has cutting-edge stack expertise. Eastern Europe offers strong talent at $50-$95/hour vs $125-$250/hour in the U.S.
Budget and Cost Considerations
Software budget encompasses more than development: cloud infrastructure, third-party services, licensing, maintenance, and scaling costs.
Most founders underestimate total costs by 40-60%. Here’s why:
Cloud costs vary dramatically. Serverless reduces expenses for low-traffic apps ($50-$200/month) but becomes expensive at scale ($3,000-$8,000/month for high traffic). Traditional servers provide predictable costs ($500-$2,000/month) with upfront investment.
AI capabilities? API-based services (OpenAI, Anthropic) charge per token – expect $500-$2,000/month for moderate usage. Self-hosting needs GPU infrastructure ($1,000-$5,000+ monthly) plus DevOps expertise.
Database licensing: PostgreSQL and MySQL are free. Oracle and SQL Server cost thousands to hundreds of thousands annually. Managed services (AWS RDS, MongoDB Atlas) add 20-40% but eliminate operational overhead.
Hidden costs that surprise teams:
- Payment processing fees: Stripe/PayPal charge 2.9% + $0.30 per transaction
- Monitoring tools: DataDog, New Relic cost $300-$1,500/month
- CI/CD services: GitHub Actions, CircleCI add $200-$800/month
- CDN costs: Cloudflare, AWS CloudFront charge $100-$500/month for global delivery
Real budget example: A project quoted at $120,000 for development had actual first-year costs of $156,000 when including infrastructure ($18,000), third-party services ($12,000), and security audits ($6,000).
Time to Market Pressures
Speed often trumps perfection for MVPs. Frameworks with built-in features accelerate development. Ruby on Rails, Django, and Laravel let small teams ship in 8-12 weeks vs 6+ months.
Why this matters: Two startups raised funding simultaneously. Startup A chose a lean stack (Django + React) and launched their MVP in 10 weeks. Startup B built with microservices “for future scale” and needed 6 months. Startup A acquired 5,000 users and validated product-market fit while Startup B was still building. By launch, Startup A had 18 months of user feedback and iteration advantage.
Decision framework for speed vs. sophistication:
Choose speed (lean stack): If you’re pre-product-market-fit, fundraising depends on traction, competitors are moving fast, or budget is limited.
Choose sophistication: If you’re proven business scaling up, technical debt will cost more than delay, or regulatory requirements demand robust architecture upfront.
Low-code platforms gain traction. By 2026, 80% of low-code users work outside IT. 48% report faster builds, 45% report reduced costs. However, they hit limitations with complex custom logic or unique integrations.
Security and Compliance Requirements
Security considerations vary dramatically by industry. Getting this wrong has legal and financial consequences.
Healthcare (HIPAA): End-to-end encryption, audit logging, strict access controls. Violations cost $100-$50,000 per record breached. Financial services (PCI DSS): Payment processing standards. Non-compliance blocks you from accepting credit cards.
European customers (GDPR): Compliant data handling regardless of server location. Fines reach €20 million or 4% of global revenue – whichever is higher.
How this affects your stack: Some frameworks provide better security defaults. Django includes built-in protection against SQL injection, XSS, and CSRF attacks. Spring Boot offers comprehensive security modules. Node.js requires more manual configuration, increasing vulnerability risk without careful implementation.
Practical example: A SaaS company chose Node.js without implementing proper security middleware. Six months post-launch, a security audit found 14 critical vulnerabilities. Remediation cost $85,000 plus 3 months of development time – time their competitor used to gain market share.
Maintenance and Long-term Support
Long-term viability matters as much as current capabilities. Technologies with strong communities, regular updates, and mature ecosystems age gracefully.
Why you should care: A company built their platform on a trendy framework in 2020. By 2023, the framework had declining adoption, slow security updates, and shrinking talent pool. They faced two bad choices: continue with risky tech or spend $200K rebuilding. Neither option was good.
Check adoption trajectory. React shows continued growth. Angular maintains enterprise usage. Vue gains traction. Older frameworks like Backbone show decline.
Maintainability indicators:
- GitHub: 1,000+ stars, commits within last month, issues resolved within 7 days
- Stack Overflow: 10,000+ questions indicate strong community
- Job market: Growing postings signal healthy ecosystem (check 12-month trends)
- Corporate backing: Meta (React), Google (Angular) provide stability
- Documentation: Comprehensive, updated within 6 months, includes migration guides
Red flags signaling future problems:
- Last major release over 18 months ago
- Declining GitHub activity or contributor exodus
- Job postings down 20%+ year-over-year
- Security patches taking 60+ days
Current Tech Stack Trends Shaping 2026

The technology landscape evolves rapidly, but certain trends define how modern applications get built in 2026.
Understanding these shifts helps you make forward-looking decisions – choices that won’t feel outdated in 12 months.
AI-Powered Development Tools
AI moved from buzzword to backbone. 84% of developers use AI tools, with 51% using them daily. This isn’t optional – it’s competitive advantage.
Code Generation: GitHub Copilot, Cursor AI, and ChatGPT reduce boilerplate by 30-40%. Developers complete features 25-35% faster. In 2025, 41% of all code written is AI-generated.
Automated Testing: AI generates test cases, improves coverage from 60-70% to 80-90%.
Code Review & Security: AI catches 63% more vulnerabilities than manual review.
ROI Example: A 5-person team using AI tools ($500-$800/month) sees 25% productivity increase worth $15,000-$25,000 monthly.
Stack implications: Favors languages with extensive training data. Strongest: JavaScript, Python, Java, TypeScript. Limited: Newer languages (Rust, Elixir).
Serverless and Cloud-Native Architecture
Serverless eliminates infrastructure management. Cloud-native development with microservices and containers defines modern architecture.
However, not universal. Well-designed monoliths suit early startups. Modular monoliths fit growing products. Microservices fit large organizations. Start small, split when pain points emerge.
Edge Computing and Global Performance
Edge computing brings computation closer to users, reducing latency. Cloudflare Workers, AWS Lambda@Edge process requests at edge locations worldwide.
Consider for: Global user bases, latency-sensitive apps, high-volume real-time data.
Integration of AI/ML Capabilities
AI integration shifted from optional to expected. 53% of U.S. tech jobs require AI/ML skills.
However, AI adds 20-30% to costs through API fees, GPU infrastructure, specialized talent, and data pipelines. Factor into total cost of ownership.
Understanding trends is valuable, but trends alone won’t help you make the right choice. You need a systematic decision-making process.
That’s what the next section provides – a proven 7-step framework that takes you from requirements to decision with confidence.
Step-by-Step Framework for Choosing Your Tech Stack
Most tech stack guides tell you what to choose. This framework shows you how to choose.
The difference? Following a “what to choose” list gets you a stack that works for someone else. Following a “how to choose” framework gets you a stack optimized for your specific situation.
This is the same framework used by companies that successfully scaled from MVP to millions of users without a single costly rewrite.
Step 1: Define Your Project Requirements
Begin with clarity. Vague requirements create bloated budgets and missed deadlines.
Document core business objectives with targets. Identify target users (demographics, devices, locations). Prioritize features: Must-Have (MVP critical), Important (Phase 2), Nice-to-Have (Future).
Example requirement definition:
Business objective: Launch B2B scheduling platform to reduce enterprise meeting coordination time by 40%. Target: Acquire 50 enterprise customers ($10K+ ARR each) within 12 months.
Target users: Operations managers and executive assistants at 100-1,000 person companies. Primary devices: Desktop browsers (80%), mobile (20%).
Must-Have features: Calendar integration (Google, Outlook), availability finder, automated scheduling, email notifications, basic analytics.
Important (Phase 2): Video conferencing integration, advanced analytics, team scheduling, API access.
Nice-to-Have: AI scheduling assistant, mobile apps, custom branding.
Define non-functional requirements with numbers: expected traffic, required uptime (99.9% = 8.7 hours downtime/year), response times, compliance needs (GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2).
This clarity eliminates 50% of scope creep and prevents building features nobody asked for.
Step 2: Assess Current Team Capabilities
Honestly evaluate team skills. What languages and frameworks do they know well? Consider team size – small teams (2-5) benefit from full-stack frameworks. Larger teams can specialize.
Factor hiring plans. Training takes 2-6 months. Hiring common tech (React, Node.js) takes 30-60 days. Rare skills require 3-6 months.
Step 3: Research and Shortlist Technologies
Create shortlist of 2-3 potential stacks. Research ecosystem maturity, community size, documentation quality, adoption trends.
But how do you separate signal from noise?
Use objective criteria: GitHub activity, Stack Overflow questions, job postings, developer surveys. Evaluate learning curves and total costs (tools, hosting, licensing).
Step 4: Build a Proof of Concept
Validate before committing. Build small POC implementing your most complex or risky feature.
What should you test in your POC?
Test critical questions: Can it handle your data volume? Does it integrate with required services? Can your team build with it productively?
Specific things to validate:
- Performance: Load test with realistic data volumes (if you expect 10,000 records, test with 50,000)
- Integration: Connect to your required third-party services (payment processors, analytics, CRMs)
- Developer Experience: Can your team write code efficiently? Are errors easy to debug?
- Deployment: How long does it take to deploy? Is the process smooth or frustrating?
Time-box to 1-2 weeks. Focus on technical validation, not production code.
Example POC scope: A fintech company testing Node.js vs. Python validated: (1) Processing 1,000 transactions/second, (2) Integrating with Plaid API, (3) Implementing fraud detection logic, (4) Deploying to AWS. This 10-day POC revealed Python’s data libraries gave them 40% faster development for fraud detection – making the decision clear.
Document what you learn. What worked well? What created friction? Would you confidently recommend this stack to your team?
Step 5: Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership
Calculate 3-5 year TCO: development (40-50%), QA/testing (15-25%), design (10-20%), project management (10-15%), infrastructure, maintenance, scaling.
Concrete TCO example – SaaS Platform:
Year 1 (MVP Launch):
- Development: $120K
- Infrastructure: $600/month × 12 = $7.2K
- Third-party services: $400/month × 12 = $4.8K
- Security audit: $6K
- Total Year 1: $138K
Year 2 (1,000 → 10,000 users):
- New features: $60K
- Infrastructure: $2,500/month × 12 = $30K
- Third-party APIs: $1,200/month × 12 = $14.4K
- Maintenance: $20K
- Total Year 2: $124.4K
Year 3 (10,000 → 50,000 users):
- Feature expansion: $40K
- Infrastructure: $8,000/month × 12 = $96K
- APIs and services: $2,800/month × 12 = $33.6K
- Performance optimization: $25K
- Total Year 3: $194.6K
3-Year TCO: $457K (vs. $120K initial quote)
Model realistic growth scenarios. Calculate infrastructure scaling, API consumption costs, licensing fees. Build spreadsheets with conservative, expected, and optimistic scenarios.
Step 6: Consider Future Growth and Flexibility
Think beyond immediate needs to 3-5 year vision. Choose architectures allowing gradual evolution. Modular monoliths can split into microservices later.
Real flexibility example: An e-commerce company built their checkout flow tightly coupled with Stripe. Two years later, they needed to add PayPal and Apple Pay for international expansion. The rewrite cost $45K and took 3 months. A competitor using a payment abstraction layer added new processors in 2 weeks for $8K.
Questions to ensure flexibility:
- Can we swap databases without rewriting application logic?
- Can we add payment processors without major refactoring?
- Can we move from one cloud provider to another if needed?
- Can we transition from monolith to microservices incrementally?
Evaluate vendor lock-in risks. Cloud-specific services (AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions) offer convenience but create migration challenges. Open-source alternatives provide flexibility but require more operational effort.
The balance: Use cloud services for non-critical features (file storage, email) where switching is easy. Keep critical business logic provider-agnostic.
Step 7: Make the Decision and Document It
Commit to a decision. Indecision costs more than imperfect choices.
Document decision and reasoning: Why this stack? What factors mattered most? What alternatives were rejected and why?
Create technical guidelines: coding standards, architectural patterns, testing requirements, deployment procedures.
You now have a systematic framework for evaluating tech stacks. But you might be wondering: “What are other successful companies actually using?”
Let’s look at proven combinations that work in 2026 – not to copy them blindly, but to understand the patterns that make them successful.
Popular Tech Stack Combinations for 2026
While every project has unique needs, certain stack combinations prove particularly effective for common use cases in 2026.
Think of these as battle-tested templates, not rigid rules.
Understanding these patterns provides starting points. But here’s what matters more than specific technologies: understanding WHY each combination works for its use case. That’s what lets you adapt intelligently rather than copy blindly.
MERN Stack (MongoDB, Express, React, Node.js)
The MERN stack remains highly popular, powering startups to enterprises. JavaScript throughout the stack reduces context switching and enables seamless full-stack development.
What are the advantages?
Unified Language: JavaScript everywhere means faster onboarding, easier knowledge sharing, smaller team size.
A 3-person team can cover full-stack work requiring 5-6 specialists traditionally.
Massive Ecosystem: npm offers 2+ million packages. Need authentication? Use Passport.js. Real-time features? Socket.io integrates natively.
JSON-Based Data Flow: Data moves as JSON from MongoDB → Express → React without transformation.
Real-World Implementations: Netflix (200+ million subscribers), Uber (millions of real-time requests), PayPal (35% faster response times)
Best Use Cases: SPAs, real-time apps (chat, dashboards), content platforms, API-driven applications
Performance: 50-200ms API response times, <50ms real-time latency, handles 10,000+ concurrent users per instance
Sounds perfect? Not quite.
Limitations: JavaScript lacks compile-time type checking (add TypeScript for $5K-$15K). MongoDB’s eventual consistency may not suit strict ACID requirements (consider PostgreSQL).
Cost: Development $60K-$150K, hosting $200-$2,000/month, developer rates $80-$150/hour
When to choose MERN:
- You need rapid development and iteration
- Real-time features are critical (chat, collaboration, live updates)
- Your team knows JavaScript well
- You want one language across the full stack
When NOT to choose MERN:
- Complex relational data with multiple joins
- Financial transactions requiring strict ACID compliance
- CPU-intensive tasks (video encoding, image processing)
- Team has zero JavaScript experience (6-month learning curve)
Other Popular Combinations
Python + Django/Flask: Excels for AI integration, data processing, rapid prototyping. Used by Instagram (1 billion+ users), Spotify (streaming 100 million tracks), Dropbox.
When to choose: Building AI-powered features, heavy data processing, you need rapid development with batteries-included framework, team has Python expertise.
Cost implications: Development faster than Java/C# (20-30% less time). AI integration costs $500-$2,000/month for APIs. Python developers: $90-$160/hour.
JAMstack (JavaScript, APIs, Markup): Incredible performance through CDN-served static files, enhanced security, easy scaling. Used by Airbnb (marketing pages), Nike (content sites), Figma (landing pages).
When to choose: Content-heavy sites, marketing pages, documentation sites, blogs, e-commerce with relatively static catalogs. NOT suitable for: highly dynamic dashboards, real-time collaborative tools, apps requiring server-side processing.
Cost advantage: Hosting $0-$100/month (dramatically cheaper than traditional servers). Development $40K-$80K for content sites.
Cloud-Native Kubernetes Stack: Ultimate scalability for high-traffic apps serving millions. Spotify (500M+ users), Airbnb (150M+ users), Pinterest (450M+ users).
When to choose: You’re serving millions of users, need independent service scaling, have dedicated DevOps team, multi-tenant SaaS requiring isolation.
When NOT to choose: Early-stage startup, team <10 developers, simple CRUD applications. Overkill = wasted resources.
AI-First Stack (Python + FastAPI + LangChain): Specialized for AI-powered applications. Prioritizes async processing, vector databases (semantic search), prompt engineering workflows.
Real applications: AI chatbots, document analysis tools, recommendation engines, AI-augmented SaaS platforms.
Cost reality: Higher than traditional stacks. OpenAI API: $0.03-$0.06 per 1K tokens. Anthropic Claude: $0.015-$0.075 per 1K tokens. Vector databases (Pinecone): $70-$400/month. Total AI costs: $1,000-$5,000+/month for moderate-use applications.
Now you understand proven patterns and frameworks. But knowledge alone doesn’t guarantee success.
Even experienced teams fall into predictable traps. Let’s examine the most expensive mistakes so you can avoid them.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced teams make predictable errors. The good news? These mistakes follow patterns.
Following Trends Blindly
Choosing technologies based on hype rather than fit is the most common failure.
Real Example: Fintech startup chose Elixir because it was “hot.” Result: Couldn’t hire developers (4 months vs 30 days for Node.js), lacked libraries, $45,000 rewrite cost. Total: $120,000+ wasted, 6 months lost.
How to avoid: Require 2-3 years production usage, stable releases, growing communities, rising job demand.
Over-Engineering Early
Premature optimization extends timelines 40-60% and wastes resources.
Real Example: E-commerce startup built Kubernetes microservices expecting “millions.” Reality: 200 users after 6 months. Cost: $180K vs $75K for monolith. Time: 9 months vs 4 months.
| Architecture | Cost | Timeline |
| Monolith | $60K-$100K | 3-5 months |
| Microservices | $150K-$300K | 8-12 months |
When to add complexity: Only when experiencing measurable pain (slow queries, long deployments, 10K+ concurrent users).
Other Critical Mistakes
Ignoring Team Skills: Unfamiliar tech extends timelines 30-50%. For MVPs, favor existing strengths.
Operational Complexity: Managed services cost 20-40% more but eliminate ops burden for small teams.
Long-term Costs: Model 3-5 years including infrastructure, maintenance, scaling – not just development.
Personal Preferences Over Business Needs: Let business requirements drive decisions, not resume building.
No Change Planning: Build abstractions allowing component swaps. Document decisions for future maintainers.
You now have the framework, the patterns, and awareness of the pitfalls. But there’s one more question many teams face: “Should we do this ourselves or get expert help?”
The answer depends on your situation. If you’re time-constrained, navigating unfamiliar territory, or the stakes are high (enterprise systems, regulated industries), expert guidance often pays for itself by avoiding costly mistakes.
How Bitcot Supports Tech Stack Selection and Implementation
Choosing the right tech stack is just the first challenge. The harder part? Implementing it correctly without expensive mistakes.
Bitcot specializes in helping businesses navigate complex technology decisions and execute implementations that deliver measurable value. We’ve guided 200+ companies through tech stack decisions – from startups validating MVPs to enterprises modernizing seven-figure legacy systems.
What We Provide
Technology Assessment: Comprehensive tech stack evaluation with comparison matrices, TCO projections, risk assessments, and POC planning. We analyze your unique situation – team capabilities, budget, timeline, and strategic goals.
Custom Development: End-to-end development across all major stacks (MERN, Python/Django, Cloud-Native, AI-powered). We follow industry best practices: 80-90% test coverage, comprehensive API documentation, security-first architecture, CI/CD pipelines.
Scaling & Optimization: Performance audits, database optimization (60-80% faster), caching strategies (40-60% load reduction), monitoring setup, and cloud cost optimization (25-45% savings).
Team Augmentation: Skilled developers productive within 1-2 weeks. 30-40% less than full-time hiring. Plus training programs for your internal team.
Why Companies Choose Us
200+ successful projects across healthcare, fintech, eCommerce, SaaS. 4.8/5.0 client satisfaction. Technology agnostic recommendations. Business outcome focus (time to market, revenue impact, operational efficiency). Transparent communication with weekly reports. Flexible engagement models.
Recent Client Outcomes: Healthcare SaaS achieved HIPAA compliance, launched 6 weeks ahead of schedule, stayed within budget. View our case studies for detailed project results.
Ready to make technology decisions with confidence? Contact Bitcot for a customized technology roadmap aligned with your business goals.
Conclusion
Choosing the right tech stack in 2026 is a balancing act between speed, cost, scalability, and long-term sustainability. Teams must ship quickly without creating technical debt, control rising development costs, and ensure their stack can support growth over the next 3–5 years.
At the same time, the stakes are higher than ever. Global IT and software spending continues to rise, while AI integration alone adds 20–30% to development costs. Poor decisions now often lead to expensive rewrites, hiring delays, and missed market opportunities.
So what separates successful teams from the rest?
From 200+ real-world implementations, one pattern stands out. Winning teams don’t chase trendy technologies. Instead, they make systematic decisions grounded in business goals, real constraints, and team capabilities.
Key Takeaways – Your Tech Stack Checklist
- Start with business outcomes, not tools
- Choose technologies your team can build with today
- Model 3–5 year total cost of ownership
- Validate assumptions with focused proof of concepts
- Plan for evolution, not perfection
- Factor in hiring realities and AI productivity gains
At its core, technology is an enabler, not the outcome. The right tech stack is the one that delivers your product on time, within budget, meets user needs, and supports sustainable growth.
The most successful founders and CTOs follow a similar approach. They start simple, validate early, and scale deliberately. When the stakes are high, they often partner with teams that have navigated these decisions many times before.
That leads to the real question.
It’s not whether you’ll choose a tech stack. It’s whether you’ll choose it systematically, or rely on guesswork.
Your Next Steps
If you’re planning:
Document requirements, shortlist 2–3 stack options, and calculate realistic 3-year TCO projections.
If you’re building:
Define a focused MVP, select proven frameworks, and plan development milestones carefully.
If you’re scaling:
Audit your current stack, identify performance or cost bottlenecks, and prioritize changes based on ROI.
If you want expert guidance, Bitcot’s consultants bring 15+ years of experience and have helped 200+ companies make confident tech decisions. We reduce risk, eliminate guesswork, and accelerate execution.
Schedule your free 30-minute tech stack consultation today for unbiased, practical guidance aligned with your business goals and budget. Contact Bitcot Now →












