
The global mHealth apps market is projected to grow from $40.65 billion in 2025 to $88.70 billion by 2032. That is not a typo. Healthcare technology is experiencing a tectonic shift, and every digital health solution needs a backend that is fast, secure, and built for scale.
So when someone asks, “What is the best programming language for healthcare app development?” the answer keeps circling back to one technology that has quietly powered the web for over three decades.
PHP.
It powers over 75% of all websites with a known server-side language. It runs platforms like WordPress, Slack’s backend infrastructure, and countless EHR portals used by hospitals across the United States. And yet, founders and CTOs still wonder, “Is PHP still relevant for building healthcare applications in 2026?”
Short answer – yes, more than ever. Here is why that is the case, and what you need to know before choosing your tech stack.
This guide breaks it all down. From HIPAA-compliant architecture and framework selection to real-world use cases and cost advantages, this is everything a decision-maker needs to know about using PHP for healthcare app development.
Let us start with the foundation.
Why PHP Still Dominates Web Development in Healthcare
PHP has been around since 1994. That kind of longevity is not accidental.
“Languages come and go with hype cycles, but the ones that survive three decades do so because they solve real problems at scale. PHP is not trendy. It is trusted, and in healthcare, trust is everything.”
The language continues to evolve. PHP 8.x brought Just-In-Time compilation, named arguments, match expressions, and fiber-based concurrency. These are not minor improvements. They translate directly into faster processing times, cleaner code, and better scalability for data-intensive healthcare applications.
Can PHP handle large-scale healthcare applications? Absolutely. PHP already supports some of the most traffic-heavy platforms on the internet. When a hospital’s patient portal needs to handle thousands of simultaneous requests for appointment scheduling, lab results, and prescription refills, PHP’s performance benchmarks hold up.
Here is what keeps PHP relevant for health tech teams:
- Open-source and cost-effective: No licensing fees, which matters when healthcare budgets are tight.
- Massive developer pool: Finding experienced PHP developers is significantly easier than sourcing talent for niche languages.
- Framework maturity: Laravel, Symfony, and CodeIgniter offer enterprise-grade tooling out of the box.
- Database flexibility: PHP integrates seamlessly with MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and other databases commonly used in healthcare data management.
- Cross-platform compatibility: PHP applications run on Linux, Windows, and macOS servers without modification.
The question is not whether PHP can do the job. It is whether your team knows how to leverage it properly for healthcare-specific requirements. As healthcare digital transformation accelerates across the United States, choosing the right backend language is a strategic decision, not just a technical one.
For anyone researching how to build an online health care system in PHP, the foundation starts with understanding these core advantages. But advantages alone do not build compliant software. The real differentiator lies in how PHP’s features map to healthcare-specific demands.
Key Features of PHP That Support Healthcare App Development
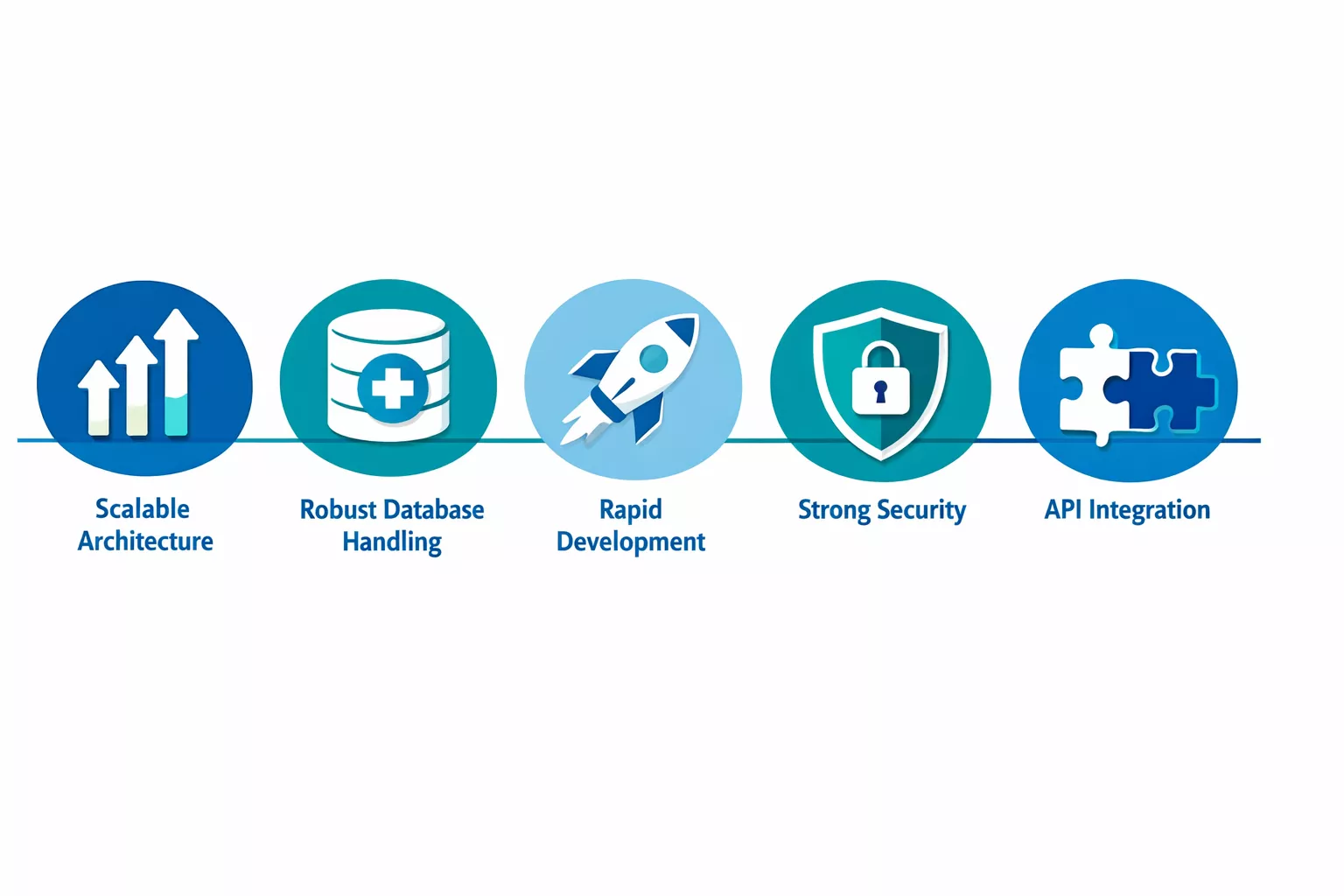
Healthcare software is not like building a standard SaaS product. The compliance requirements are stricter. The data sensitivity is higher. And the consequences of failure are measured in patient safety, not just revenue.
PHP addresses these challenges with a feature set that aligns naturally with healthcare needs, whether you are building hospital management systems, telehealth platforms, or patient-facing portals.
Scalable Architecture for Growing Patient Loads
Hospitals and clinics do not stay the same size forever. A PHP application built on Laravel or Symfony can scale horizontally using load balancers and cloud infrastructure. This makes PHP a strong foundation for cloud-based healthcare applications where your EHR system or telemedicine platform can grow without a complete rewrite.
Scaling is only half the equation, though. What about the data itself?
Robust Database Handling
Healthcare applications manage enormous volumes of structured data. Patient records, insurance claims, diagnostic results, and billing information all require reliable database operations. PHP’s native support for MySQL, SQLite, PostgreSQL, and ODBC connections makes it a strong fit for data-driven healthcare platforms.
With strong data handling in place, the next concern for most product teams is speed to market.
Rapid Development Cycles
“How long does it take to build a healthcare app with PHP?” This is one of the most common questions from founders and product leaders. With frameworks like Laravel, a minimum viable product for a clinic management system in PHP Laravel or an appointment scheduling platform can be delivered in 8 to 16 weeks, depending on complexity.
PHP frameworks come with built-in authentication, routing, caching, and ORM tools. Developers are not building from scratch. They are assembling proven components, which drastically reduces time to market and enables healthcare workflow automation from day one.
Strong Security Foundations
PHP 8.x includes built-in protections against common vulnerabilities like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and cross-site request forgery (CSRF). When combined with Laravel’s encryption and hashing modules, PHP applications can meet the stringent security requirements that healthcare regulators demand.
Easy Integration With Third-Party APIs
Modern healthcare apps need to talk to multiple external systems. Healthcare interoperability is no longer a nice-to-have. Whether it is HL7 FHIR for health data exchange, payment gateways for billing, or wearable device APIs for remote patient monitoring, PHP’s RESTful API capabilities make integration straightforward and maintainable.
Features are one thing. Regulatory survival is another. And in healthcare, nothing matters more than compliance.
How PHP Supports HIPAA Compliance
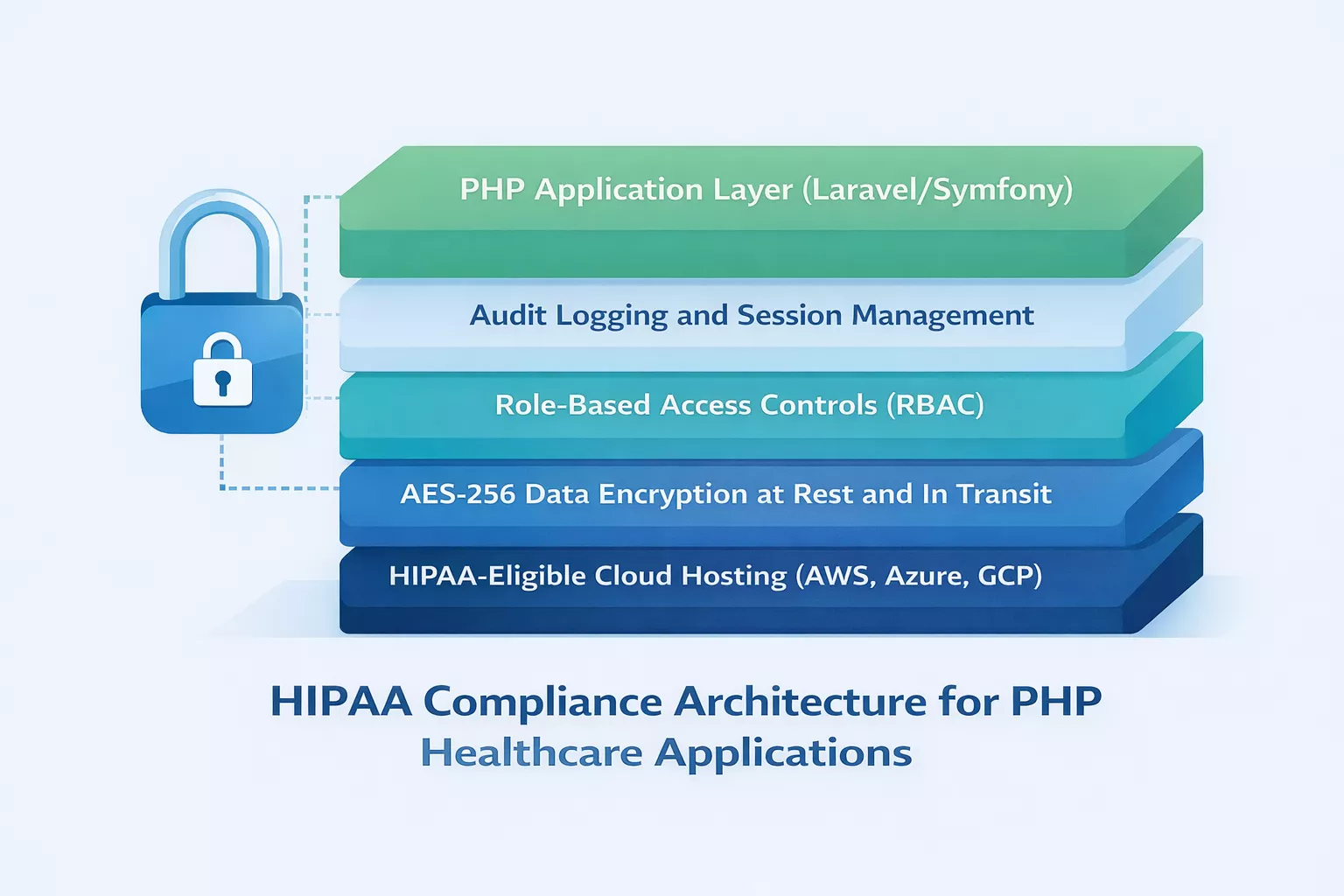
If you are building a healthcare application in the United States, HIPAA compliance is not optional. It is the baseline. Miss it, and you face fines up to $2,190,294 per violation category as of January 2026. And this is where many development teams stumble.
“Is PHP HIPAA compliant?” PHP itself is a programming language. No language is inherently HIPAA compliant. Compliance is about how you architect the application, handle data, manage access, and configure your hosting environment.
That said, PHP provides every tool needed to build HIPAA-compliant applications when patient data security is treated as a core requirement.
Data Encryption: PHP supports AES-256 encryption through OpenSSL, and Laravel’s built-in encryption uses AES-256-CBC by default. Patient health information (PHI) can be encrypted both at rest and in transit.
Access Controls: Role-based access control (RBAC) is straightforward to implement in PHP frameworks. Doctors, nurses, administrative staff, and patients can each have distinct permission levels.
Audit Logging: Every access, modification, and deletion of PHI needs to be logged. PHP frameworks support middleware-based logging that captures these events automatically.
Secure Session Management: PHP handles session management natively, and frameworks add layers like token-based authentication, OAuth 2.0 support, and multi-factor authentication.
Hosting Considerations: The application code is only part of the equation. HIPAA compliance also requires BAA (Business Associate Agreement) with your hosting provider. AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure all offer HIPAA-eligible services that pair well with PHP deployments. Understanding how to migrate a Laravel PHP application to AWS with the right security architecture can make or break your compliance posture.
“Compliance is not a feature you bolt on at the end. It is an architectural decision you make on day one. The organizations that treat HIPAA as a design principle, not a checklist, are the ones that avoid seven-figure penalties.”
Building a HIPAA-compliant healthcare app is not just about checking boxes. It is about creating an architecture where patient data is protected at every layer. And the architecture starts with one decision that shapes everything else – which PHP framework you build on.
Best PHP Frameworks for Healthcare Applications
Choosing the right framework is one of the most important technical decisions in any healthcare project. The framework dictates your development speed, security posture, and long-term maintainability.
Here is a comparison of the top PHP frameworks for healthcare app development:
| Framework | Best For | Key Strengths | Learning Curve |
| Laravel | Full-featured healthcare platforms | Eloquent ORM, built-in auth, queues, encryption | Moderate |
| Symfony | Enterprise-grade hospital systems | Modular components, long-term support, flexibility | Steep |
| CodeIgniter | Lightweight clinic portals | Small footprint, fast performance, simple setup | Low |
| CakePHP | Rapid prototyping of health MVPs | Convention over configuration, scaffolding tools | Low to Moderate |
| Yii 2 | High-performance data applications | Lazy loading, caching, security features | Moderate |
Why Laravel Leads for Healthcare
Laravel has become the default choice for most PHP-based healthcare applications, and for good reason. Its Artisan CLI, Blade templating engine, and Eloquent ORM reduce development time significantly. Laravel Passport and Sanctum handle API authentication cleanly, which is essential for mobile health apps that connect to backend services.
“Should I use Laravel or Symfony for a healthcare app?” For most healthcare startups and mid-sized organizations, Laravel offers the best balance of speed, security, and developer productivity. Symfony is better suited when you need granular control over every component, which is more common in a large enterprise hospital management system.
The framework matters. But what really convinces stakeholders is proof. Here is where PHP is already doing the heavy lifting.
Real-World Use Cases of PHP in Healthcare

PHP is not just a theoretical fit for healthcare. It is already powering critical health technology platforms across the industry. Not experimental pilots. Production systems. Serving real patients, real clinicians, and real claims every single day.
Electronic Health Record (EHR) Systems
EHR and electronic medical records (EMR) platforms need to store, retrieve, and update patient records in real time. PHP’s database handling capabilities, combined with Laravel’s queue system for background processing, make it ideal for building responsive EHR interfaces that clinicians actually want to use.
Beyond records management, healthcare delivery itself has gone digital.
Telemedicine and Virtual Care Platforms
Telemedicine is now a permanent pillar of healthcare delivery, not a pandemic workaround. PHP-based backends handle video consultation scheduling, e-prescribing, and secure messaging between patients and providers. Integration with WebRTC for video calls and HL7 FHIR for clinical data exchange is well-supported. Organizations exploring telehealth website development often find that PHP offers the fastest path from concept to compliant platform.
Patient Portal Development
“How do I build a patient portal?” This is a question nearly every health system asks at some point. PHP excels here. A patient portal built with Laravel can include appointment booking systems, lab result viewing, prescription refills, secure messaging, and billing. All behind role-based authentication.
Pharmacy Management Systems
Inventory tracking, prescription processing, drug interaction alerts, and insurance verification are all data-intensive operations. PHP handles these workflows efficiently, especially when paired with MySQL for transactional data and Redis for caching.
The financial side of healthcare is equally demanding.
Health Insurance and Claims Processing
Insurance companies and third-party administrators use PHP-based platforms to process claims, verify eligibility, and manage provider networks. The language’s ability to process large datasets quickly makes it suitable for these batch-heavy operations.
Remote Patient Monitoring Dashboards
Wearable devices and IoT sensors generate continuous streams of health data. A health monitoring management system built with PHP can ingest this data through REST APIs, process it, and display it on real-time dashboards for care teams to monitor patient vitals remotely.
With all these use cases covered, the natural follow-up question is whether PHP is truly the best option or if another language does it better.
PHP vs Other Languages for Healthcare App Development
Decision-makers often ask, “Should I choose PHP, Python, or Node.js for my healthcare application?” Fair question. Each language has trade-offs. The answer depends on your specific requirements, but here is how they stack up head to head:
| Factor | PHP | Python | Node.js |
| Server-side web apps | Excellent | Good | Good |
| AI/ML integration | Limited | Excellent | Moderate |
| Real-time features | Good (with WebSockets) | Moderate | Excellent |
| Developer availability | Very High | High | High |
| Healthcare ecosystem | Strong (EHR, portals) | Strong (analytics, AI) | Growing |
| Development cost | Lower | Moderate | Moderate |
| Framework maturity | Very High | High | High |
PHP wins on cost efficiency, developer availability, and framework maturity for traditional healthcare web applications. Python is the better choice when AI and machine learning are core to the product. Node.js excels in real-time applications like live chat and monitoring dashboards.
Many modern healthcare platforms use PHP for the core application layer while integrating Python microservices for analytics and AI features. This hybrid approach gives you the best of both worlds.

So PHP checks the boxes on capability. The next question every founder and CTO asks is simpler but just as important – what will this actually cost?
Cost of Building a Healthcare App With PHP
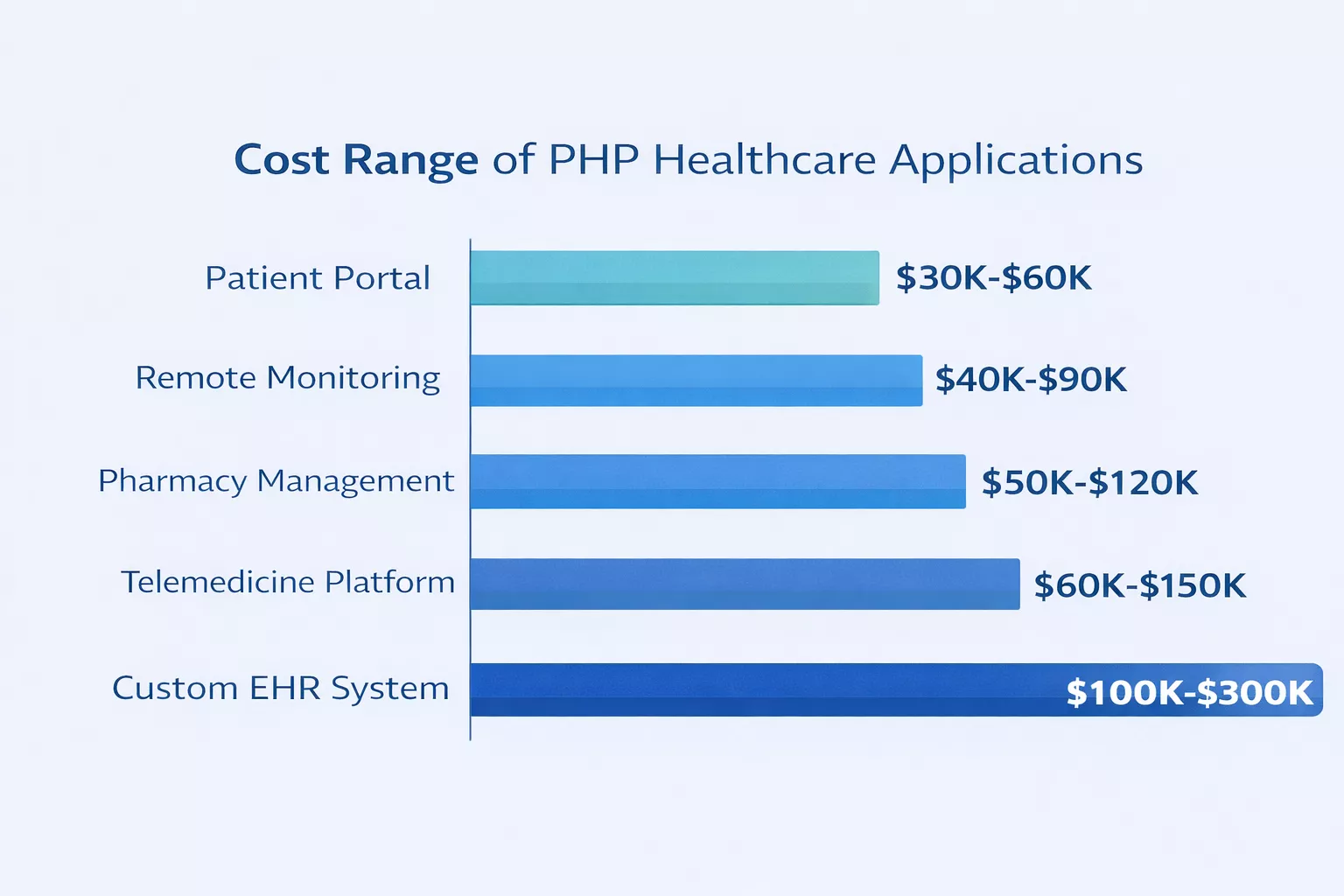
Budget is always a factor. “How much does it cost to build a healthcare app using PHP?” Here is a realistic breakdown based on application complexity:
| App Type | Estimated Timeline | Estimated Cost Range |
| Basic patient portal | 8 to 12 weeks | $30,000 to $60,000 |
| Telemedicine platform | 12 to 20 weeks | $60,000 to $150,000 |
| Custom EHR system | 20 to 36 weeks | $100,000 to $300,000 |
| Pharmacy management system | 12 to 24 weeks | $50,000 to $120,000 |
| Remote monitoring dashboard | 10 to 16 weeks | $40,000 to $90,000 |
These estimates assume a dedicated development team, HIPAA-compliant hosting, and proper QA testing. PHP’s open-source nature and extensive library ecosystem help keep costs lower compared to proprietary alternatives.
Remember to budget for ongoing maintenance, which typically runs 15% to 20% of the initial development cost annually. Skip this line item, and you will pay for it later.
Numbers tell one side of the story. But even the right budget cannot protect you from avoidable mistakes.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using PHP for Healthcare Apps
Even experienced teams make critical errors when building healthcare applications. Most of them are preventable. Here are the most common pitfalls:
Ignoring HIPAA from the start: Retrofitting compliance is exponentially more expensive than building it in from day one. Access controls, encryption, and audit logging should be part of the initial architecture.
Choosing the wrong framework: Not every PHP framework is suited for healthcare. A lightweight framework like CodeIgniter might work for a simple clinic website but will struggle under the demands of a full EHR platform.
Skipping security testing: Healthcare applications are prime targets for cyberattacks. Regular penetration testing, code reviews, and vulnerability scanning are non-negotiable.
Neglecting mobile optimization: Over 60% of patients access health portals from mobile devices. A PHP backend must support responsive frontend interfaces and mobile API endpoints.
Underestimating integration complexity: Connecting with legacy hospital systems, insurance databases, and lab information systems requires careful API planning and often HL7/FHIR expertise.
Avoiding these mistakes is easier when you work with a team that has already navigated them.
How Bitcot Builds PHP-Powered Healthcare Solutions
Building a healthcare application is not just a coding exercise. It requires deep domain expertise, compliance knowledge, and a development partner who understands the stakes.
Bitcot has completed 3,000+ projects, including healthcare organizations that need secure, scalable, and regulation-ready web and mobile applications.
The Bitcot team follows HIPAA guidelines and leverages PHP frameworks like Laravel, Symfony, CodeIgniter, and CakePHP to build healthcare platforms that meet real clinical and operational needs.
From custom EHR development and telemedicine software to patient portals and pharmacy management systems, Bitcot’s approach starts with a discovery phase that maps your clinical workflows, compliance requirements, and growth objectives before a single line of code is written.
The healthcare web application development process is built around the realities of medical software development, where security and usability must coexist from the first sprint.
Whether you are a startup building an MVP or an enterprise modernizing legacy systems, Bitcot’s PHP development services combine technical depth with healthcare-specific experience to deliver applications that work for providers, patients, and administrators alike.
“In healthcare, the technology you choose has to earn trust every single day. We build with PHP because it gives our clients the performance, security, and flexibility to deliver care without compromise.”
– Raj Sanghvi, Founder and CEO, Bitcot
With the right technology and the right partner in place, the path forward becomes clear.
Conclusion
Healthcare app development is not a space where you can afford to get the technology decision wrong. The backend you choose affects everything, from how quickly you reach the market to whether your application survives its first HIPAA audit. This guide covered the critical factors that every founder, CTO, and product leader should weigh before committing to a tech stack.
PHP brings a combination of advantages that few other languages match for healthcare. An open-source ecosystem that keeps development costs lower. Frameworks like Laravel and Symfony that provide enterprise-grade security, authentication, and database management out of the box. A developer talent pool large enough that scaling your team does not become a bottleneck.
Native support for AES-256 encryption, role-based access controls, and audit logging that aligns directly with HIPAA requirements. And a three-decade track record that proves PHP can handle production-scale healthcare systems, from EHR platforms and telemedicine applications to patient portals and insurance claims processing.
The mHealth market is projected to more than double by 2032. Healthcare organizations that invest in the right technology stack now will be the ones leading digital health transformation in the years ahead.
With PHP 8.x continuing to improve performance and developer experience, the language is only getting stronger. Keeping pace with emerging healthcare technology trends is essential, and PHP, when paired with the right framework, the right architecture, and the right development partner, delivers on that promise.
If you are evaluating technology options for a healthcare application, the next step is straightforward. Start with a discovery phase that maps your clinical workflows, compliance needs, and growth goals before writing a single line of code.
Looking to build a healthcare application that is secure, scalable, and built following HIPAA guidelines? Talk to the Bitcot team today and start your discovery project before committing to a full development contract. No pitch decks. No pressure. Just a technical conversation about what your healthcare product actually needs.












