If you’ve visited a doctor lately, chances are some part of that experience felt different than it did even a few years ago.
Maybe you booked your appointment online, checked in with a QR code, spoke to a provider over video, or saw your lab results instantly on a mobile app. That’s not just convenience; it’s the result of digital transformation in healthcare.
In 2025, this shift isn’t optional anymore.
U.S. healthcare organizations are investing billions into digital health solutions, with telehealth adoption holding strong post-pandemic and AI-powered tools becoming part of everyday clinical workflows. Patients, especially Millennials and Gen Z, are pushing for seamless, tech-driven experiences that match what they already get from banking, shopping, or travel apps.
On the other side, healthcare leaders are under pressure to cut costs, combat clinician burnout, and keep up with regulatory demands. The message is clear: staying paper-based or relying on outdated systems isn’t just inconvenient; it’s a competitive disadvantage.
This guide gives you a full 360° view of how digital transformation is reshaping healthcare in the U.S. right now. From core software like EHRs and hospital management systems, to mobile apps that connect patients with providers, to AI solutions that are redefining diagnostics, billing, and even drug discovery, we’ll explore the technologies, drivers, benefits, and risks of going digital.
We’ll also look at global comparisons, U.S. success stories, and what the next decade could bring, from digital twins to quantum-powered drug research.
Whether you’re a hospital CEO planning the next big investment, a startup founder building the next healthcare app, or a clinician wondering how AI might actually make your day easier, this guide will help you cut through the buzzwords and see what digital transformation really means in 2025, and how you can act on it.
Why Digital Transformation is Reshaping U.S. Healthcare in 2025

Let’s start with the big picture: the numbers.
In 2024, U.S. digital health funding crossed $15 billion, and telehealth visits remained at levels five times higher than before COVID-19.
Far from being a temporary fix during the pandemic, digital health has become a permanent pillar of how care is delivered. By 2025, patients and providers alike aren’t just experimenting with technology; they’re expecting it.
So, why can’t healthcare leaders ignore this anymore?
Because digital transformation is no longer about “nice-to-have” tools, it’s about survival and growth.
CEOs, CTOs, and hospital administrators are under intense pressure to meet rising patient expectations, reduce clinician burnout, streamline operations, and comply with new regulatory frameworks. Falling behind in digital maturity doesn’t just mean inefficiency; it can mean losing patients, losing staff, and losing ground to competitors who are moving faster.
Also Read: Top 15+ Healthcare Technology Trends in 2025: The Future of Medical Innovation
At the heart of this transformation are three core pillars:
- Healthcare Software that powers hospitals, clinics, and research organizations.
- Mobile Apps that keep patients engaged, connected, and in control of their care.
- AI Solutions that help providers work smarter, diagnose faster, and personalize treatment.
Together, these pillars aren’t just improving how healthcare operates; they’re redefining the very experience of care delivery.
COVID-19 was the great accelerator. What started as an emergency response, like telehealth consults, remote patient monitoring, and digital prescriptions, has now solidified into everyday practice. Patients who got used to convenience aren’t willing to go back, and providers who embraced digital workflows are seeing long-term benefits in efficiency and patient satisfaction.
The competitive landscape also tells a clear story. Healthcare organizations that are digital-first are consistently outperforming those clinging to legacy models. They attract more patients, operate more efficiently, and deliver better outcomes. Meanwhile, traditional systems are struggling with slower adoption, higher costs, and mounting frustration from both staff and patients.
Zooming out, the U.S. is racing to keep pace with other developed nations. Countries like Estonia and Denmark have already built fully digital health ecosystems with nationwide interoperability. While the U.S. has made strides, fragmentation across providers and systems means there’s still work to do. The global comparison makes one thing clear: U.S. healthcare organizations that embrace digital transformation now will not only catch up but potentially leapfrog competitors on the world stage.
Finally, there’s the demographic shift. Millennials and Gen Z now make up a large portion of the patient population, and they’ve grown up in a digital-first world. They don’t want faxed prescriptions or phone-only scheduling.
They expect mobile-first access, telehealth options, and AI-enabled personalization, just like they get from Amazon, Uber, or their banking apps. Their expectations are reshaping the very definition of “quality care.”
In short, 2025 is the year digital transformation stops being optional. It’s the year where software, apps, and AI aren’t just supporting healthcare; they’re leading it.
What is Digital Transformation in Healthcare and Why It Matters
“Digital transformation” is one of those phrases that gets thrown around a lot, but what does it really mean in healthcare?
At its core, it’s not just about adding a new app or moving files to the cloud. It’s about rethinking how care is delivered, how patients interact with providers, and how technology is used to improve outcomes, lower costs, and make the system more sustainable.
Think of it like this:
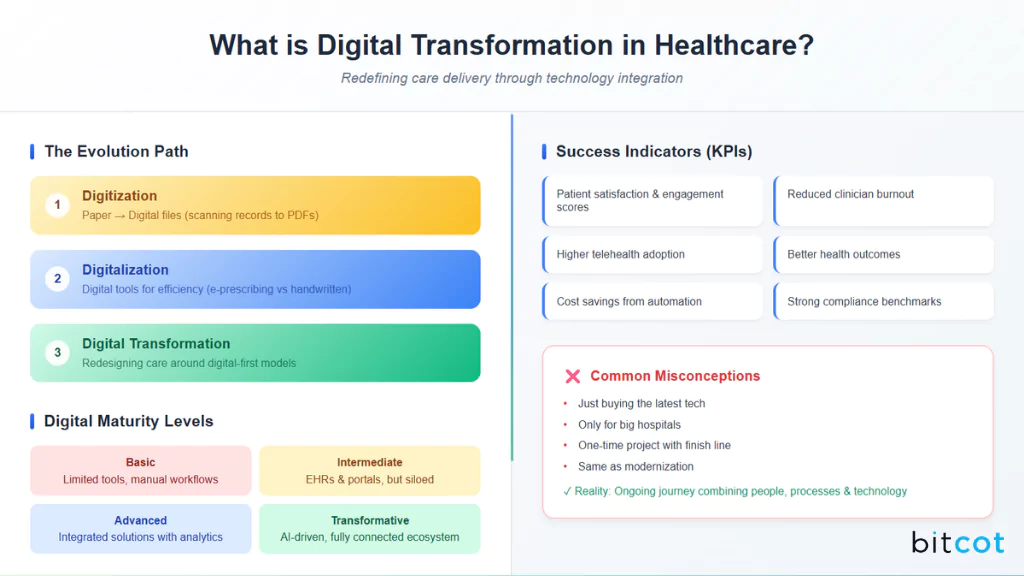
- Digitization is the first step, turning paper into digital files (like scanning medical records into PDFs).
- Digitalization goes further, using digital tools to make processes faster or more efficient (like electronic prescribing instead of handwritten scripts).
- Digital transformation is the big leap; it’s about redesigning healthcare around digital-first models, where software, mobile apps, AI, and connected devices work together to deliver care in ways that weren’t possible before.
The evolution of healthcare technology tells this story well. We’ve gone from stacks of paper charts → to EMRs and EHRs → to cloud platforms enabling interoperability → and now to AI-driven healthcare that predicts, personalizes, and even automates care. Each stage didn’t just add convenience; it reshaped how patients and providers interact.
But here’s an important distinction: digital transformation isn’t the same as modernization. Upgrading an old hospital system or installing a new billing module is modernization; it keeps things current. Transformation, on the other hand, is about a mindset shift. It’s about asking: How can we leverage technology to deliver care in entirely new ways?
How do you know if digital transformation is actually working? That’s where Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) come in.
Some common markers include:
- Improved patient satisfaction and engagement scores.
- Reduced clinician burnout and admin workload.
- Higher telehealth adoption rates.
- Better health outcomes (e.g., fewer hospital readmissions).
- Cost savings from automation and efficiency.
- Strong compliance and data security benchmarks.
Healthcare organizations often measure progress using digital maturity levels:
- Basic: Limited digital tools, mostly manual workflows.
- Intermediate: Core systems digitized (EHRs, portals), but still siloed.
- Advanced: Integrated solutions across departments with analytics and automation.
- Transformative: AI-driven, predictive, and fully connected ecosystem; digital-first is the default.
Along the way, there are plenty of misconceptions that hold organizations back. Some leaders think digital transformation is just about buying the latest tech. Others believe it’s only for big hospitals or that it’s a one-time project with a finish line.
The reality?
It’s an ongoing journey that combines people, processes, and technology, and it’s as much about culture change as it is about software.
In short, digital transformation matters because it’s not just upgrading healthcare; it’s redefining it. And the organizations that embrace this shift will be the ones shaping the future of patient care.
What Drives Healthcare Digital Transformation in the U.S.: Key Factors

If you ask five different healthcare leaders why they’re investing in digital transformation, you’ll probably hear five different answers.
But together, these reasons reveal the bigger picture: the U.S. healthcare system is under pressure from all sides: patients, regulators, payers, providers, and even technology itself.
Let’s break down the main drivers fueling this change.
- Rising patient expectations (digital-first care): Patients no longer compare their healthcare experience only to other hospitals; they compare it to Amazon, Netflix, or Uber. They want 24/7 access, easy scheduling, transparent pricing, and mobile-first care options. Digital-first has become the default expectation, especially for younger generations.
- Regulatory pressure: The rules are changing fast. HIPAA remains the cornerstone of data privacy, but new CMS interoperability rules, FDA digital health guidance, and state-level telehealth laws are pushing organizations to modernize their systems. Staying compliant often requires adopting new digital tools and workflows.
- Staff shortages & clinician burnout: The U.S. faces a critical shortage of doctors and nurses, while existing staff are burning out under heavy administrative burdens. Automation, AI documentation tools, and digital scheduling platforms are no longer just efficiency upgrades; they’re lifelines for workforce sustainability.
- Cost reduction & efficiency goals: Healthcare is expensive, and everyone, from patients to insurers to hospital boards, is demanding more value for less money. Digital tools like RPA (robotic process automation), AI-driven analytics, and cloud platforms help cut waste, reduce duplicate tests, and streamline billing.
- Post-pandemic telehealth boom: COVID-19 proved that virtual care works. Even after emergency mandates expired, patients and providers kept using telehealth for convenience, speed, and safety. This “telehealth stickiness” continues to push hospitals, insurers, and startups to expand digital care offerings.
- Value-based care mandates: Healthcare is shifting from fee-for-service to value-based models where providers are rewarded for outcomes, not volume. That requires strong digital infrastructure: analytics for measuring results, AI for risk stratification, and apps for patient engagement.
- Population health & social determinants of health: Chronic disease management, mental health, and preventive care all demand better data collection and digital insights. Population health platforms help track not just medical records, but also social determinants like housing, food security, and transportation that directly affect outcomes.
- Healthcare consolidation: Mergers and acquisitions are creating massive health systems that need standardized digital platforms across multiple sites. Interoperability, cloud adoption, and unified EHRs become essential when dozens of hospitals and clinics need to “speak the same digital language.”
- Environmental sustainability: Sustainability is no longer just a corporate buzzword; it’s a healthcare priority. Hospitals are looking at digital solutions for energy management, paperless workflows, and carbon footprint tracking, aligning with broader ESG (environmental, social, governance) goals.
- Health insurance evolution: Insurance models are changing. Alternative payment models, consumer-driven health plans, and digital-first insurers (like Oscar Health) are pressuring providers to adapt. Patients now expect seamless digital claims, real-time benefits tracking, and transparent billing.
- Pharmaceutical industry needs: Pharma is becoming deeply digital, using real-world evidence, wearable data, and AI-driven drug discovery. Providers and health systems must integrate with these innovations to participate in trials, partnerships, and new treatment models.
- Medical device connectivity: The FDA’s push for connected devices and breakthrough device designations is accelerating the adoption of medical IoT. From wearables to implantables, connected devices generate valuable real-time data, but only if health systems have the digital infrastructure to use it safely and effectively.
In short, U.S. healthcare isn’t transforming for just one reason; it’s transforming because every pressure point is pushing it in that direction. From patient demand to regulatory compliance to financial sustainability, digital transformation has become the only path forward.
What Technologies Power Healthcare Digital Transformation

The backbone of digital transformation in healthcare isn’t just strategy; it’s the technology stack that makes change possible.
From cloud platforms that keep records accessible to AI models that assist in diagnosis, the right tools create the foundation for modern, patient-centered care.
Let’s look at the core technologies shaping this shift:
Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Healthcare organizations are increasingly moving to the cloud for scalability, security, and interoperability. Whether it’s storing electronic health records (EHRs) or enabling cross-hospital data exchange, cloud adoption is now essential.
- Multi-cloud vs. hybrid cloud: Hospitals are mixing providers to balance costs, security, and compliance.
- Migration challenges: Legacy systems, data silos, and HIPAA compliance make moving tricky, but best practices include phased migration and encryption-first approaches.
- Cloud-native vs. cloud-enabled apps: True cloud-native solutions are built for flexibility, while cloud-enabled apps extend the life of older platforms.
- Resilience: Disaster recovery and business continuity planning are now baked into cloud strategies.
Mobile Health Apps (mHealth)
The smartphone has become a pocket-sized healthcare hub. From managing chronic conditions to offering telehealth consultations, mobile apps connect patients and providers anytime, anywhere.
- PWAs vs. native apps: Progressive Web Apps are faster to deploy, while native apps allow deeper integration with devices.
- Regulations: Apps that cross into medical device territory must meet FDA and app store requirements.
- Accessibility: ADA and WCAG compliance ensure usability for all patients, including those with disabilities.
AI & Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence is no longer futuristic; it’s at the center of modern care delivery.
- Predictive analytics & automation: Identifying high-risk patients before crises occur.
- Generative AI & LLMs: Helping physicians with clinical documentation and patient communication.
- Bias & ethics: Ensuring fairness in AI-driven diagnoses and treatments.
- Federated learning: Training AI on decentralized patient data without compromising privacy.
- Applications: Computer vision for radiology, reinforcement learning for drug dosing, and ongoing model monitoring frameworks.
IoT & Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
Connected devices allow healthcare to extend beyond the hospital walls.
- Wearables & chronic care: Smartwatches that track heart rhythms or glucose levels.
- Digital therapeutics (DTx): FDA-approved apps functioning as prescribed treatments.
- Smart home healthcare: Ambient sensors supporting elderly care at home.
- Security protocols: Strong authentication is vital as more devices connect to hospital networks.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Behind the scenes, RPA reduces administrative burden.
- Billing & claims automation: Streamlining revenue cycles.
- IPA (Intelligent Process Automation): Combining AI with RPA to handle more complex workflows.
- Governance: Healthcare requires strict oversight of bot lifecycles to maintain compliance.
5G & Edge Computing
Connectivity is the lifeblood of digital healthcare.
- Telehealth with low latency: High-quality video consultations and real-time imaging.
- Edge AI: Processing patient data locally for faster response.
- Private 5G: Hospitals deploying dedicated networks for reliability and security.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Unlocking value from unstructured medical text.
- Clinical documentation improvement: Automating note-taking and coding.
- Voice workflows: Doctors dictating notes directly into EHRs.
- Multilingual NLP: Supporting diverse patient populations in real time.
Advanced Analytics & Business Intelligence
Turning raw data into actionable insights.
- Dashboards & reports: Real-time operational views.
- Predictive modeling: Anticipating patient surges and optimizing staffing.
- Data lakes & warehouses: Consolidating clinical and financial data for deeper analysis.
What Are the Best Healthcare Software Solutions for Digital Transformation

Digital transformation in healthcare isn’t just about new technologies;it’s about putting the right software solutions in place to make hospitals, clinics, and providers more efficient, connected, and patient-centered.
Let’s explore the most impactful healthcare software categories driving this shift:
Electronic Health Records (EHR/EMR)
Electronic Health Records are the foundation of digital healthcare. They’ve evolved from simple digital charts to intelligent systems that guide clinical decisions.
- Interoperability challenges: Sharing data across providers and systems remains a hurdle.
- AI-enabled EMRs: Features like voice dictation and predictive care suggestions reduce clinician workload.
- FHIR adoption: Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) standards improve data exchange.
- Usability focus: Physician satisfaction is tied to simplified interfaces and faster workflows.
- Specialty customizations: Tailored EHRs for pediatrics, oncology, or behavioral health improve care delivery.
- Data migration: Strategies for integrating legacy systems are critical for smooth transitions.
Hospital Management Software (HMS)
HMS platforms act as the operating system for hospitals, handling both patient and administrative needs.
- Staff & resource management: Optimizing schedules and reducing clinician burnout.
- Patient flow: Bed management and discharge planning to minimize delays.
- Asset & equipment tracking: Ensuring availability and proactive maintenance.
- Facility modules: Energy management and security integration.
Telemedicine Platforms
Telemedicine has gone mainstream post-pandemic, enabling access to care anytime, anywhere.
- Core features: Secure video calls, e-prescriptions, payments, and appointment scheduling.
- HIPAA compliance: Privacy and data protection are non-negotiable.
- Hybrid models: Combining telehealth with in-person visits for continuity of care.
- Specialty use cases: Dermatology, radiology, and psychiatry lead the adoption curve.
- System integration: Linking telemedicine with EHRs, billing, and diagnostic tools.
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
CDSS provides clinicians with evidence-based guidance at the point of care.
- AI-driven insights: Helping with diagnostics and personalized treatments.
- Drug interaction checks: Reducing errors and improving safety.
- Guideline automation: Embedding evidence-based medicine into workflows.
- Clinical alerts: Delivering real-time notifications for critical decisions.
- Pathway optimization: Standardizing care while allowing personalization.
Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) Software
RCM ensures the financial health of providers by streamlining billing and payments.
- Automation: Claims processing, prior authorizations, and fraud detection.
- Denial management: Reducing lost revenue through proactive tracking.
- Patient experience: Transparent billing, payment plans, and cost estimators.
- Eligibility checks: Instant insurance verification to reduce administrative delays.
Pharmacy Management Systems
Modern pharmacy platforms go beyond prescription refills.
- Inventory & tracking: Monitoring stock levels to prevent shortages.
- Telepharmacy & MTM: Supporting remote consultations and medication therapy management.
- Automation & robotics: Speeding up dispensing and reducing human error.
- Pharmacogenomics: Tailoring prescriptions based on genetic profiles.
Population Health Management Platforms
Population health tools help organizations shift to value-based care.
- Risk stratification: Identifying high-risk groups for early intervention.
- Care gap detection: Tracking missed screenings or follow-ups.
- SDOH tracking: Incorporating social determinants like housing or income into care strategies.
- Quality reporting: Meeting payer and regulatory requirements.
Care Coordination Platforms
These solutions bridge communication gaps across providers and settings.
- Team collaboration: Enabling multi-disciplinary care planning.
- Care plan management: Aligning treatment across inpatient, outpatient, and home care.
- Referral management: Streamlining specialist consultations and follow-ups.
Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS)
LIMS solutions keep labs running efficiently and compliant.
- Sample tracking: Automating workflows from collection to results.
- Equipment integration: Directly linking diagnostic machines to digital records.
- Quality control: Ensuring regulatory compliance and accuracy.
Imaging and PACS Systems
Medical imaging is one of the biggest beneficiaries of digital transformation.
- Workflow optimization: Storing and sharing high-volume imaging data.
- AI-powered analysis: Assisting radiologists with early detection.
- Mobile & cloud access: Enabling clinicians to review scans from anywhere.
What Are the Most Effective Healthcare Mobile Apps for Patients and Providers
Mobile apps are at the heart of healthcare’s digital transformation.
From managing daily health routines to streamlining provider workflows, apps bridge the gap between care delivery and modern patient expectations.
Let’s look at the most effective types of healthcare mobile apps shaping the industry today.
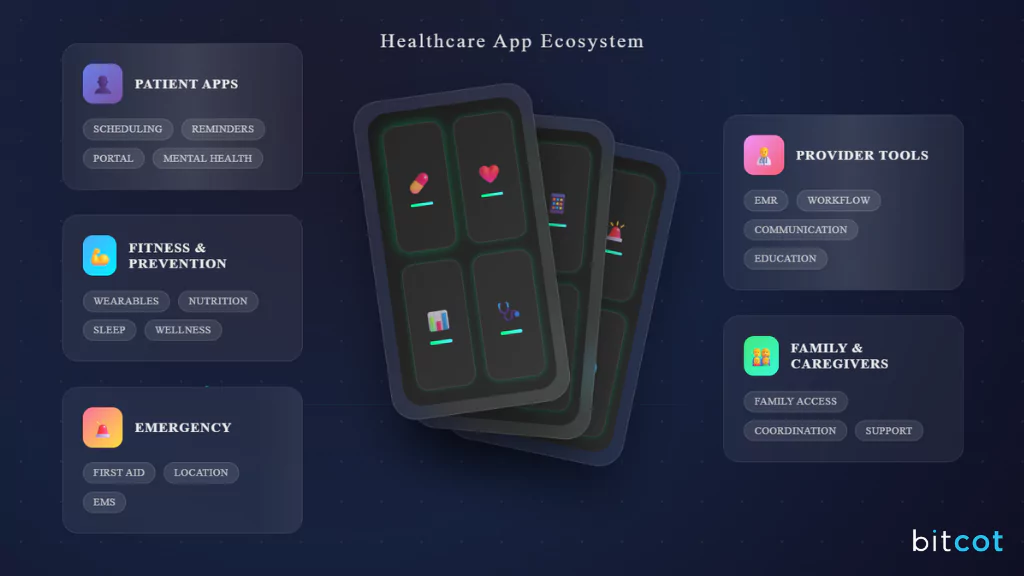
Patient-Facing Apps
Patients today expect the same simplicity from healthcare apps that they get from their favorite social or banking apps. The most effective solutions combine convenience, engagement, and personalization.
- Scheduling & reminders: Book appointments, set medication alerts, and track follow-ups.
- Chronic disease care: Apps for diabetes, asthma, or heart disease help patients monitor vitals and share data with providers.
- Mental health: Guided meditation, CBT-based tools, and teletherapy integrations are becoming mainstream.
- Patient portal integration: Unified access to lab results, visit summaries, and secure messaging with clinicians.
- Social features: Peer support communities encourage patients to share progress and stay motivated.
- Gamification: Reward systems for medication adherence or healthy lifestyle changes.
- Multilingual & cultural support: Apps tailored to diverse populations improve accessibility.
- Offline functionality: Vital for rural or underserved areas with poor internet access.
Provider-Facing Apps
For clinicians, mobile apps reduce friction, save time, and improve care accuracy.
- Mobile EMR access: Quick retrieval of patient histories at the bedside.
- Workflow tools: Streamlined charting, documentation, and order entry.
- Clinical communication: Secure messaging platforms to replace unsecure texting.
- Decision support apps: Drug reference guides and AI-driven diagnostic suggestions.
- Shift scheduling & tracking: Staff can swap shifts, track hours, and manage workloads.
- Education apps: Ongoing training, CME credits, and certification tracking in mobile formats.
Fitness & Preventive Care Apps
Prevention is the new frontier of healthcare, and fitness apps are leading the charge.
- Wearable integration: Sync with smartwatches and trackers for activity, heart rate, and sleep.
- Lifestyle tracking: Nutrition, hydration, stress, and exercise monitoring.
- Corporate wellness programs: Employer-sponsored apps that reward healthy behavior.
- HSA integration: Linking wellness incentives directly to Health Savings Accounts.
- Nutrition & meal planning: AI-based diet recommendations and grocery list automation.
- Sleep optimization: Apps that track circadian rhythms and recommend sleep hygiene improvements.
Caregiver and Family Apps
Healthcare often involves more than the patient; it’s about the whole care ecosystem.
- Family access: With consent, loved ones can track appointments, meds, and progress.
- Caregiver support: Tools to assess caregiver stress and provide resources.
- Coordination tools: Pediatric and elderly care apps help families stay aligned on treatment plans.
Emergency and First Aid Apps
In urgent situations, mobile apps can save lives.
- Emergency coordination: Location-based services that connect users to nearby hospitals or urgent care.
- First aid guidance: Step-by-step instructions for CPR, wound care, or allergic reactions.
- EMS integration: Direct connections to emergency services for faster response times.
- Contact management: Store and auto-dial emergency contacts when needed.
How AI & Automation Transform U.S. Healthcare Operations

AI and automation are no longer “nice-to-have” experiments in healthcare; they’re becoming the backbone of modern operations. From the front desk to the operating room, these technologies are streamlining processes, improving accuracy, and making care more personalized.
Here’s how they’re reshaping U.S. healthcare in 2025 and beyond:
- AI Chatbots for Patient Queries & Triage: Patients expect answers fast, and AI chatbots are meeting that demand. These digital assistants handle appointment scheduling, symptom checks, FAQs, and triage, freeing up staff while providing 24/7 support.
- Predictive Analytics for Disease Prevention: AI-driven predictive models analyze EMR data, lifestyle factors, and even wearables to flag high-risk patients early, helping providers prevent diabetes, heart disease, or hospital readmissions before they happen.
- AI in Radiology & Imaging: Radiologists now work side by side with AI tools that detect tumors, fractures, or anomalies faster and sometimes more accurately than humans. This reduces errors and speeds up diagnosis.
- Virtual Nursing Assistants: Virtual nurse apps support patients at home, answering medication questions, checking symptoms, and reminding patients about post-op care instructions, bridging gaps between visits.
- RPA for Admin Tasks: Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is streamlining back-office operations such as claims processing, billing, and documentation. What once took hours of manual effort now happens in minutes with higher accuracy.
- AI-Powered RPM with IoT Devices: Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) paired with AI makes it possible to track vitals in real-time. For example, heart monitors can alert providers when a patient’s risk level spikes, triggering early interventions.
- Clinical Trial Matching & Recruitment: AI automates the complex process of identifying eligible patients for trials by scanning EHRs and medical histories, helping pharmaceutical companies speed up research while ensuring diversity.
- AI-Powered Drug Discovery: Machine learning accelerates drug development by predicting molecule interactions, reducing R&D time and costs. What once took years can now be shortened dramatically.
- Automated Coding & Clinical Documentation Improvement (CDI): AI tools assist in coding patient encounters correctly, reducing billing errors and ensuring compliance. Clinical documentation improvement systems also auto-suggest details clinicians may have overlooked.
- AI Ethics & Governance: As AI expands, hospitals are setting up AI ethics committees to monitor bias, transparency, and compliance. Governance frameworks ensure AI recommendations are explainable and clinically sound.
- Explainable AI for Decision Transparency: Clinicians need to trust AI decisions. Explainable AI (XAI) allows providers to see why an algorithm made a recommendation, building confidence in adoption.
- AI-Powered Scheduling & Resource Allocation: AI optimizes OR schedules, staff shifts, and resource use to minimize delays and improve hospital efficiency, critical in large health systems with high patient volume.
- Personalized Treatment Plan Generation: AI integrates genomic data, clinical history, and lifestyle factors to create customized care pathways, moving from one-size-fits-all to precision medicine.
- AI-Driven Infection Control: Hospitals are using AI to predict infection outbreaks, track antibiotic usage, and optimize stewardship programs to combat resistance and improve patient safety.
Why Digital Transformation Benefits Every Healthcare Stakeholder

One of the reasons digital transformation has unstoppable momentum in U.S. healthcare is that it doesn’t just benefit one group; it lifts the entire ecosystem.
From patients to regulators, every stakeholder gains something valuable when technology is embedded into care delivery and operations.
- Patients: Patients are the ultimate beneficiaries. Digital tools bring faster appointment scheduling, 24/7 telehealth, medication reminders, and personalized treatment plans. With unified records and wearable integration, care becomes proactive, not reactive.
- Providers: Physicians and nurses get relief from repetitive admin tasks through RPA, AI-powered documentation, and mobile EMR access. Decision-support tools also help providers diagnose and treat patients more efficiently, improving both outcomes and job satisfaction.
- Hospitals & Clinics: Health systems cut down on duplicative tests, optimize bed management, and improve patient flow. Cloud platforms and automation reduce overhead while unlocking operational efficiency.
- Insurers: Insurers benefit from AI-powered fraud detection, automated claims processing, and real-time eligibility verification. Patients enjoy smoother billing experiences, while insurers gain lower losses and faster reimbursements.
- Pharma: Pharmaceutical companies speed up clinical trials using digital recruitment and AI analytics. Real-world evidence from wearables and EHRs also improves post-market research and drug innovation.
- Public Health: Digital health data helps public health agencies spot disease patterns, predict outbreaks, and allocate resources quickly. Lessons from COVID-19 have made digital surveillance a permanent fixture in population health.
- Healthcare Ecosystem: FHIR standards, APIs, and cloud adoption enable smoother data exchange between hospitals, labs, pharmacies, and insurers. This connected ecosystem supports continuity of care across all stakeholders.
- Society: Telehealth and mobile apps expand access for rural and underserved communities. Digital health literacy programs and multilingual tools help bridge cultural and economic divides.
- Regulators: Digital reporting systems make compliance monitoring more efficient. Regulators benefit from real-time dashboards and automated reporting, helping enforce HIPAA, CMS, and FDA standards with greater accuracy.
- Medical Device Manufacturers: Device makers use IoT data to track performance, detect issues, and optimize future products. Post-market surveillance powered by AI and blockchain strengthens patient safety and regulatory compliance.
The takeaway? Digital transformation creates a win-win scenario across the board; patients receive better care, providers work more efficiently, and the entire healthcare ecosystem becomes smarter, safer, and more connected.
What Are the Main Challenges & Risks in Digital Healthcare Adoption

While digital transformation promises enormous benefits, the journey isn’t without roadblocks. Healthcare organizations often find themselves walking a tightrope between innovation and risk.
Let’s break down the biggest challenges that leaders need to address when adopting digital healthcare solutions.
- Data Privacy & HIPAA Compliance: Protecting sensitive patient data is priority number one. Every digital system, from mobile apps to EHRs, must comply with HIPAA and other privacy frameworks. A single breach not only damages trust but can result in hefty fines.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Healthcare is a prime target for cybercriminals. Ransomware, phishing, and IoT device hacks are on the rise. Without strong cybersecurity frameworks, zero-trust models, and proactive monitoring, hospitals risk both data loss and operational downtime.
- High Upfront Implementation Costs: Modernizing infrastructure, integrating AI, and migrating to the cloud can carry significant upfront expenses. While the ROI often pays off in the long run, smaller practices may struggle with initial funding.
- Staff Resistance & Training Gaps: Doctors, nurses, and administrators may resist change, especially if the new tech feels complex or time-consuming. Comprehensive training, user-friendly design, and change management strategies are critical for adoption.
- The Digital Divide – Rural vs. Urban Access: Not all patients have equal access to broadband, devices, or digital literacy. Rural communities in particular may be left behind without dedicated efforts to bridge the gap.
- Algorithm Bias & Health Equity Concerns: AI can unintentionally reinforce biases if trained on incomplete or skewed datasets. This creates risks for underrepresented groups, leading to inequitable care. Building fairness and transparency into algorithms is essential.
- Vendor Lock-In & Integration Complexities: Switching EHR providers or integrating with legacy systems is often painful. Vendor lock-in can limit flexibility, increase costs, and slow innovation if contracts aren’t structured carefully.
- Regulatory Compliance Across Jurisdictions: Healthcare organizations operating across state or national borders must navigate a complex maze of regulations. HIPAA, GDPR, FDA, and other frameworks often overlap, making compliance a moving target.
- Digital Literacy Gaps Among Patients & Providers: Even the best tools fail if people don’t know how to use them. Older patients, low-income populations, and even some clinicians may struggle with digital tools unless proper education and support are provided.
- Clinical Liability & Malpractice Risks: Who’s responsible if an AI tool makes a diagnostic error? Legal frameworks are still catching up to digital transformation, leaving providers exposed to new liability risks.
- Change Management & Workflow Disruption: Adopting new systems often disrupts established routines. Without careful change management, digital initiatives can slow down staff productivity instead of improving it.
- Data Quality & Standardization Challenges: EHRs, wearables, and mobile apps generate mountains of data, but if that data isn’t standardized or high-quality, it’s more noise than insight. Interoperability is still a major hurdle.
- Technology Obsolescence & Upgrade Planning: Healthcare moves slowly, but technology evolves fast. Systems risk becoming outdated within just a few years, requiring continuous upgrades and flexible IT planning.
- Cross-Border Data Sharing & International Compliance: As global healthcare collaboration grows, so do compliance challenges. Sharing patient data across countries requires navigating a patchwork of international privacy and security laws.
- Cybersecurity Deep Dive: Healthcare is a prime target for cyberattacks. Organizations must address common threats like ransomware, phishing, and IoT device vulnerabilities, implement zero-trust security architectures, and maintain robust incident response and business continuity plans.
- Ethical Considerations: AI and digital tools must follow ethical guidelines, including transparent and explainable decision-making, ensuring fairness and non-discrimination, and respecting patient consent and data ownership rights.
How Digital Tools Solve Real-World Healthcare Problems

Digital transformation isn’t just a buzzword; it’s a practical, lifesaving set of tools that addresses real challenges in healthcare.
From patients managing chronic conditions at home to hospitals optimizing workflows, technology is bridging gaps and improving outcomes across the board.
- Telehealth for non-emergency care: Patients can now consult doctors for common illnesses, like the flu, minor infections, or follow-ups, without leaving home. This reduces clinic congestion, saves time, and improves access to care.
- Digital tools for minor injuries: Apps and remote guidance help patients manage cuts, sprains, and minor injuries, often avoiding unnecessary emergency room visits.
- Chronic disease management: Wearables, mobile apps, and connected devices help monitor diabetes, hypertension, COPD, and other chronic conditions, giving patients and clinicians real-time insights and actionable data.
- Reducing clinician workload: AI-powered workflow automation, from documentation to billing, frees up clinicians’ time so they can focus more on patient care and less on administrative tasks.
- Mental health crisis management: Digital interventions, teletherapy, and crisis hotlines make mental health support more accessible, timely, and personalized.
- Rural healthcare access: Mobile health units, telemedicine, and connected devices bring quality care to underserved rural populations, overcoming the barriers of distance and limited local resources.
- Emergency response coordination: Real-time communication platforms allow hospitals, EMS teams, and first responders to coordinate efficiently during emergencies, improving patient outcomes in critical situations.
- Medication adherence support: Smart packaging, automated reminders, and app-based tracking help patients take medications correctly, reducing complications and hospital readmissions.
- Addressing workforce shortages: AI-driven tools assist with scheduling, triage, and task delegation, helping hospitals manage clinician shortages without compromising care quality.
- Reducing health disparities: Targeted digital interventions, telehealth, and culturally tailored apps ensure equitable care for diverse patient populations.
- Preventive care enhancement: Predictive analytics and early warning systems identify at-risk patients, enabling proactive care that can prevent diseases or complications before they become severe.
- Accelerating clinical research: Digital data collection, remote monitoring, and AI analysis streamline clinical trials and research studies, enabling faster insights and innovations.
What Can We Learn from U.S. Healthcare Digital Success Stories

When it comes to digital transformation in healthcare, the U.S. offers plenty of examples of organizations that are getting it right.
By examining these success stories, healthcare leaders can identify strategies, best practices, and lessons learned that can be applied to their own digital journeys.
- Mayo Clinic: Mayo Clinic has been at the forefront of using AI to support diagnostics. By integrating AI into imaging and pathology workflows, they’ve improved diagnostic accuracy and reduced turnaround times, enhancing patient outcomes.
- Cleveland Clinic: Cleveland Clinic rapidly scaled telehealth services during and after the pandemic, demonstrating how virtual care can maintain continuity while increasing patient access and convenience.
- Kaiser Permanente: Kaiser Permanente emphasizes patient-centered digital tools, from mobile apps to online portals, that allow patients to schedule appointments, access medical records, and engage in preventive care.
- Startups: Smaller innovators are tackling niche problems with remarkable agility. Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) devices, mental health apps, and chronic disease management platforms illustrate how startups can quickly create solutions that traditional systems sometimes struggle to implement.
- Geisinger Health: Geisinger Health leverages AI to stratify patient populations, identify care gaps, and optimize interventions, demonstrating the power of predictive analytics for improving health outcomes on a large scale.
- Intermountain Healthcare: By using integrated data systems and analytics, Intermountain Healthcare has improved operational efficiency and clinical decision-making, showing how data-driven strategies enhance both patient care and organizational performance.
- Epic vs. Cerner: The experiences of these EHR giants highlight the importance of careful planning, clinician engagement, and interoperability in large-scale system rollouts; lessons that are invaluable for any organization adopting or upgrading its EHR.
- Rural health network digital transformation success stories: Several rural networks have successfully implemented telemedicine, mobile health units, and connectivity solutions, proving that digital tools can overcome geographic and resource barriers.
- Specialty practice digital adoption: Specialty practices like dermatology, cardiology, and oncology are leveraging digital tools for remote monitoring, AI-assisted diagnostics, and personalized treatment plans, demonstrating that even niche areas benefit from digital transformation.
- Children’s hospitals digital transformation initiatives: Pediatric hospitals are using gamified apps, virtual care platforms, and patient portals to engage young patients and families while improving treatment adherence and outcomes.
- Academic medical centers research and innovation programs: Centers like Johns Hopkins and Stanford are integrating AI, big data, and cloud platforms into research programs, accelerating clinical studies, and pioneering new treatments.
- Community health centers digital equity programs: Community health centers are bridging the digital divide by implementing telehealth, patient portals, and culturally tailored apps, ensuring underserved populations receive equitable care.
Digital transformation isn’t limited to big hospitals; from startups to rural networks, every organization can find innovative ways to enhance care, improve efficiency, and engage patients.
What Does the Future of Digital Healthcare Look Like (2025 and Beyond)

Healthcare is entering an era where technology and medicine are increasingly inseparable.
By 2025 and beyond, digital tools, AI, and advanced computing will transform not just how care is delivered, but how it’s conceived, planned, and optimized.
Here’s a look at the innovations shaping the future:
- AI agents in hospital workflows: Intelligent AI assistants will handle routine tasks such as patient triage, scheduling, and preliminary diagnostics, freeing clinicians to focus on complex decision-making and patient interactions.
- Fully automated digital front doors: Patients will experience seamless digital access, from appointment booking to virtual check-ins and automated billing, creating a frictionless care experience.
- Predictive hospitals & digital twins: Hospitals will use digital twins (virtual replicas of facilities and patient populations) to simulate outcomes, optimize operations, and improve patient safety. Predictive analytics will anticipate resource needs before they arise.
- Generative AI & LLM-powered assistants: Large Language Models (LLMs) will assist with clinical documentation, patient education, care plan generation, and real-time decision support, enhancing both speed and accuracy.
- Value-based care powered by digital insights: Advanced analytics and AI will drive personalized, outcome-focused care, ensuring that healthcare providers are rewarded for patient health improvements rather than service volume.
- Quantum computing in drug discovery & genomics: Quantum computing will accelerate molecular modeling and genetic analysis, shortening drug development timelines and enabling highly precise, personalized therapies.
- Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) for neurological rehabilitation: BCIs will allow patients with neurological disorders or injuries to regain control and function through direct neural interactions with digital devices.
- Personalized medicine at scale: Multi-omics integration (genomics, proteomics, metabolomics) combined with AI will enable treatment plans tailored to each patient’s unique biological makeup.
- Autonomous surgical robots & AI-assisted procedures: Robotics and AI will enhance surgical precision, minimize human error, and support remote or minimally invasive procedures.
- Global health data networks & international care coordination: Interconnected data platforms will enable worldwide sharing of patient information, facilitating global research collaboration and cross-border healthcare delivery.
- Climate-aware healthcare delivery & sustainability metrics: Hospitals will leverage data to reduce energy consumption, track carbon footprints, and design environmentally sustainable care practices.
- Space medicine & remote healthcare delivery: With space exploration advancing, remote monitoring and telemedicine solutions will be adapted for astronauts and extreme environments, driving innovations that benefit terrestrial care as well.
- Biometric authentication & continuous patient monitoring: Advanced sensors and biometric identification will ensure secure access to patient data while enabling real-time health monitoring for early detection of critical events.
- AR/VR applications in healthcare training & therapy: Immersive AR/VR environments will revolutionize medical education, surgical training, and even patient therapy, providing interactive, realistic experiences that were previously impossible.
Emerging Technology Adoption Timeline

The pace of healthcare digital transformation varies depending on technology maturity, organizational readiness, and regulatory evolution. Mapping out a clear adoption timeline helps healthcare leaders anticipate what’s coming, prioritize investments, and prepare staff for change.
Here’s what the next decade is likely to look like:
2025-2027: Mainstream AI Integration and Automation
During these years, AI will move from experimental projects to mainstream adoption in hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare settings.
Expect AI-driven tools for clinical decision support, predictive analytics for population health, and workflow automation to reduce administrative burdens. Telehealth platforms and remote patient monitoring solutions will reach widespread use, improving access and convenience for patients.
Organizations will also focus on integrating these solutions seamlessly into existing systems, ensuring interoperability, and building trust among clinicians and patients. This period is all about optimizing current processes, proving ROI, and creating a strong foundation for more advanced technologies.
2028-2030: Advanced Robotics and Quantum Computing Early Adoption
By this period, next-generation technologies such as autonomous surgical robots and quantum computing will start appearing in early adoption cycles.
Surgical robots will enhance precision and enable minimally invasive or remote procedures, while quantum computing will accelerate molecular modeling, drug discovery, and genomics research.
Healthcare organizations that experiment with these technologies early will gain advantages in operational efficiency, clinical outcomes, and research capabilities. Pilot programs and controlled rollouts will help define best practices and regulatory compliance frameworks.
2030+: Fully Integrated Digital Health Ecosystems
Looking beyond 2030, healthcare will evolve into fully connected, data-driven ecosystems.
Digital twins for patients and hospitals, AI-powered predictive hospitals, global health data networks, and continuous remote monitoring will enable proactive, personalized, and sustainable care. Interoperability across platforms, devices, and institutions will allow seamless data flow, giving clinicians, researchers, and patients real-time insights for smarter decision-making.
By this stage, healthcare will be truly predictive, preventative, and patient-centric, with technologies integrated into every aspect of care delivery, research, and population health management.
Regulatory Evolution and the Future of Digital Healthcare Compliance

As healthcare becomes increasingly digital, regulatory frameworks are evolving to keep pace with new technologies, ensuring patient safety, privacy, and ethical use of AI and digital tools.
Understanding these changes is critical for healthcare leaders planning digital transformation initiatives.
FDA Digital Health Guidance Evolution and Adaptive Pathways
The FDA has been actively updating its guidance for digital health solutions, including software as a medical device (SaMD), AI-driven diagnostics, and mobile health applications. Adaptive regulatory pathways now allow for faster approvals while maintaining safety and efficacy standards.
This is especially important for technologies like AI-based diagnostics, predictive analytics tools, and remote monitoring devices, which must balance innovation with patient safety. Hospitals and developers can leverage these frameworks to bring solutions to market faster without compromising quality or compliance.
International Regulatory Harmonization Efforts
Healthcare is increasingly global, with cross-border data sharing and multinational clinical trials becoming the norm. International bodies are working to harmonize regulations, clarify compliance requirements, and establish unified cybersecurity and data privacy standards.
Harmonization reduces complexity for global healthcare providers, supports international research collaboration, and ensures that digital health innovations can scale safely across different regions without conflicting legal requirements.
Ethics Committees and AI Governance Frameworks
With AI taking on more clinical responsibilities, from diagnostics to treatment recommendations, healthcare organizations are implementing AI ethics committees and governance structures.
These bodies oversee:
- Algorithm transparency and explainability
- Fairness and bias prevention
- Patient consent and data protection
- Accountability for AI-driven clinical decisions
Governance frameworks ensure that AI tools are ethical, equitable, and aligned with healthcare standards. They also provide a structured approach for monitoring AI performance over time, helping hospitals maintain trust with patients and regulators alike.
How to Begin Your Digital Transformation Journey: Step-by-Step Guide

Embarking on a digital transformation in healthcare can feel overwhelming, but breaking it into clear steps makes it manageable.
Here’s a practical guide for healthcare leaders, administrators, and IT teams to navigate the journey successfully.
Step 0: Leadership Alignment and Vision Development
Before any technology decisions, your leadership team needs to align on the vision for digital transformation. Define what success looks like, whether it’s improving patient outcomes, reducing operational costs, or enhancing staff experience. Clear leadership alignment ensures that every department understands the goals and can collaborate effectively.
Step 1: Assess Needs (Clinical vs. Administrative)
Identify the specific areas that require digital solutions. Clinical needs might include AI-driven diagnostics, telehealth expansion, or patient monitoring, while administrative needs could involve billing automation, scheduling, or supply chain optimization. A thorough assessment ensures technology investments address real pain points.
Step 1.5: Stakeholder Mapping and Engagement Planning
Map all stakeholders, such as clinicians, administrators, IT staff, patients, and vendors, and understand their priorities, concerns, and workflow dependencies. Early engagement helps reduce resistance to change, improves adoption rates, and ensures the transformation meets everyone’s needs.
Step 2: Define ROI Goals
Set clear metrics to measure the success of your digital initiatives. ROI can include financial savings, operational efficiency, patient satisfaction, staff productivity, or population health outcomes. Establishing these quantifiable goals early makes it easier to track progress and justify investments.
Step 3: Select the Right Tech Stack
Choose technology solutions that fit your organization’s needs, scalability requirements, and interoperability standards. Consider cloud platforms, AI tools, mobile apps, and EHR systems that integrate seamlessly into existing workflows. Your tech stack should support both current operations and future innovations.
Step 3.5: Conduct Thorough Vendor Due Diligence and Reference Checks
Before signing contracts, evaluate vendors carefully. Review case studies, client testimonials, and security certifications. Ensure the vendor can provide ongoing support, compliance guidance, and integration expertise. This step reduces risk of implementation failure and ensures long-term value.
Step 4: Partner with an Experienced Vendor
Collaborate with a vendor who has deep healthcare experience and a track record of delivering digital transformation projects. A strong partner provides strategic guidance, technical expertise, and hands-on support throughout the journey.
Step 4.5: Legal and Compliance Review Processes
Healthcare technology is tightly regulated. Conduct legal and compliance reviews to ensure your chosen solutions meet HIPAA, FDA, and other relevant standards. Address contracts, data ownership, and liability concerns early to avoid complications later.
Step 5: Pilot → Scale Rollout
Start with a pilot program in a controlled environment to test workflows, technology integration, and user adoption. Gather feedback, make necessary adjustments, and gradually scale the solution across departments or facilities. This phased approach minimizes disruption.
Step 5.5: Continuous Monitoring, Optimization, and Iterative Improvement
Digital transformation isn’t a one-time project. Continuously monitor KPIs, user feedback, and system performance. Optimize workflows, update software, and implement iterative improvements to maximize benefits over time.
Assessing Readiness and Planning for Digital Transformation

Digital transformation in healthcare isn’t just about technology; it’s about people, processes, and systems working together.
This list helps healthcare leaders evaluate their readiness, plan strategically, and ensure successful adoption.
Digital Maturity Assessment Framework
Before implementing new digital solutions, it’s essential to understand where your organization currently stands.
The digital maturity assessment evaluates three key dimensions: technology, processes, and people.
- Current state evaluation: Assess existing systems, workflows, and staff competencies. Identify which tools are outdated, where manual processes persist, and how staff interact with technology.
- Gap analysis and prioritization matrix: Determine the gaps between current capabilities and desired outcomes. Prioritize initiatives based on impact, cost, and feasibility to focus efforts where they will deliver the most value.
- Roadmap development: Create a step-by-step plan with clear milestones, success metrics, and timelines. This roadmap ensures that digital transformation efforts are organized, measurable, and aligned with strategic goals.
Change Management Best Practices
Even the most advanced technology can fail if staff are unprepared or resistant to change. Change management is critical for adoption and long-term success.
- Stakeholder engagement and communication strategies: Identify key stakeholders, including clinicians, administrative staff, and IT teams. Communicate the benefits of transformation clearly and regularly to gain buy-in.
- Training and support programs: Provide hands-on training and continuous learning opportunities. Ensure staff are confident using new systems, which reduces errors and frustration.
- Measuring and managing resistance: Track adoption rates and gather feedback. Address concerns proactively and adjust strategies to minimize resistance and maximize engagement.
Vendor Selection Criteria
Choosing the right technology partner can make or break your digital transformation journey. A thorough evaluation ensures alignment with your goals and long-term success.
- Technology capabilities and scalability: Assess whether the vendor’s solutions can integrate with existing systems and scale as your organization grows. Look for flexibility and future-proof features.
- Security and compliance validation: Confirm that the vendor meets all healthcare regulations, including HIPAA and FDA standards. Evaluate their cybersecurity protocols and data protection measures.
- Support, training, and implementation methodologies: Review the vendor’s approach to onboarding, staff training, and ongoing support. A strong vendor will guide you through implementation, help troubleshoot issues, and provide long-term optimization assistance.
This provides a practical framework for healthcare leaders to evaluate readiness, manage change, and select the right partners, setting the stage for a successful digital transformation.
What Does Healthcare Digital Transformation Cost & What’s the ROI

Investing in digital transformation is a significant decision for healthcare organizations.
While the benefits can be substantial, such as better patient outcomes, improved efficiency, and enhanced staff satisfaction, understanding costs and ROI is essential for planning and budgeting.
Average Costs of EHR, Telemedicine, and AI Systems
Healthcare technology investments vary depending on scale and complexity:
- Electronic Health Records (EHR/EMR): Costs include software licenses, hardware, integration, training, and ongoing support. Implementation can range from hundreds of thousands to millions of dollars for large hospital systems.
- Telemedicine Platforms: Expenses cover secure video systems, e-prescriptions, remote monitoring devices, and integration with existing clinical workflows. Smaller clinics may spend $50k-$200k, while enterprise-level deployments are higher.
- AI Systems: Costs depend on whether AI is embedded in diagnostics, workflow automation, predictive analytics, or virtual assistants. Licensing, customization, and staff training are additional factors.
ROI Benchmarks: Savings, Efficiency, Patient Satisfaction
ROI should be measured in both financial and operational terms:
- Cost savings from reduced administrative workloads and optimized resource allocation.
- Increased efficiency through automation, predictive scheduling, and faster clinical decision-making.
- Improved patient satisfaction from better access, convenience, and personalized care.
Payback Timelines for Hospitals & Providers
Digital transformation payback periods vary:
- Smaller clinics may see ROI in 12-24 months.
- Large hospital networks often require 2-5 years, depending on project scale and adoption rates.
- Faster ROI is possible when solutions address high-cost areas such as readmissions, staff overtime, or inefficient billing.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Analysis
Beyond upfront costs, organizations should consider:
- Maintenance, upgrades, and licensing fees.
- Staff training and change management expenses.
- Integration with legacy systems and ongoing IT support.
- Hidden costs like workflow disruption during implementation.
Financing Options: Capital Purchase, SaaS, Hybrid Models
Organizations have multiple ways to fund digital transformation initiatives:
- Capital purchase: One-time investment for software and hardware.
- SaaS (Software as a Service): Subscription-based model with predictable monthly costs and vendor-managed updates.
- Hybrid models: Combine on-premises and cloud solutions to balance cost, flexibility, and control.
Risk-Adjusted ROI Calculations and Scenario Planning
It’s important to account for uncertainties such as technology adoption rates, staff resistance, regulatory changes, and cybersecurity incidents. Scenario planning helps estimate risk-adjusted ROI, allowing leadership to make informed decisions under varying conditions.
Value-Based Care Contract Impact on ROI
Value-based care contracts emphasize quality outcomes over volume of services, which can influence ROI calculations. Digital tools that improve care coordination, population health, and preventive care can increase reimbursement and demonstrate tangible financial benefits.
ROI Measurement Methodologies and Success Metrics
Track ROI using a combination of financial and operational metrics:
- Reduction in administrative and operational costs
- Time savings for clinicians and staff
- Patient satisfaction scores and engagement metrics
- Readmission rates and clinical outcome improvements
- Staff retention and reduced burnout
Economic Impact Studies and Industry Benchmarking
Benchmarking against similar healthcare organizations and analyzing industry economic impact studies helps validate ROI expectations and guides investment prioritization. Learning from peers ensures realistic goals and identifies opportunities for maximum impact.
Financial Planning and Budgeting
Long-term planning ensures that digital initiatives remain sustainable:
- Multi-year budget planning: Allocate resources for multi-phase transformation projects.
- Cost-benefit analysis frameworks: Evaluate the financial and operational impact of each initiative.
- Grant funding and incentives: Identify federal, state, or private programs that offset costs and accelerate adoption.
Insurance and Risk Management
Managing risks protects both investment and patient safety:
- Technology insurance and liability coverage: Safeguard against system failures, data breaches, and legal exposure.
- Business interruption and cyber insurance: Ensure continuity in case of ransomware attacks, outages, or other cyber events.
- Risk mitigation strategies: Implement contingency plans, staff training, and proactive monitoring to reduce operational and financial risks.
How Bitcot Supports Healthcare Digital Transformation

At Bitcot, we understand that digital transformation in healthcare isn’t just about technology; it’s about people, processes, and delivering measurable outcomes.
Our approach is holistic, combining deep technical expertise with healthcare domain knowledge to ensure every solution drives real value for patients, providers, and organizations alike.
- Custom Healthcare Software and Mobile Apps: Tailored solutions for patient engagement, chronic care management, and provider workflows, designed to streamline operations and enhance patient satisfaction.
- HIPAA-Compliant Telemedicine Platforms: Secure virtual care systems with video consultations, e-prescriptions, and remote monitoring, fully integrated with your existing healthcare systems.
- AI Chatbots and Workflow Automation: Automate patient queries, appointment scheduling, and administrative tasks while optimizing operational efficiency across billing, claims, and documentation.
- EMR/EHR Integration with HL7 and FHIR: Seamless data exchange across platforms to improve interoperability, reduce redundant data entry, and support better clinical decision-making.
- Proven Case Studies and Client Results: Successful digital transformation projects for hospitals, clinics, and healthcare startups, delivering measurable outcomes in patient care, efficiency, and cost reduction.
- End-to-End Digital Transformation Consulting and Strategy Development: Comprehensive assessment, gap analysis, technology recommendations, and strategic roadmaps aligned with clinical, operational, and financial goals.
- Cloud Migration and Modernization Services: Secure cloud adoption, legacy system modernization, hybrid cloud strategies, and business continuity planning for highly regulated healthcare environments.
- Ongoing Support, Maintenance, and Optimization Services: Continuous system updates, security monitoring, and performance optimization to ensure digital solutions evolve with your organization’s needs.
- Compliance and Security Assessment Services: Risk audits and regulatory checks to meet HIPAA, FDA, and other healthcare compliance standards while safeguarding patient data.
- Partnership Ecosystem and Technology Integration Capabilities: Seamless integration between digital health solutions, third-party systems, and emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain.
- Training and Change Management Support Services: Comprehensive staff training, stakeholder engagement, and change management strategies to ensure smooth adoption and sustained success.
Why the Future Belongs to Digital-First Healthcare

The future of healthcare clearly belongs to organizations that embrace digital-first strategies.
The benefits of digital transformation are undeniable: faster, more accurate care, improved patient engagement, streamlined operations, and cost efficiencies.
At the same time, the risks of ignoring digital adoption are growing: outdated workflows, frustrated staff, slower decision-making, and the inability to meet patient expectations.
For healthcare leaders, 2025 marks a turning point. Technology, patient demographics, regulatory requirements, and competitive pressures are converging, making digital transformation not just an option but an imperative for survival and growth.
Partnering with Bitcot allows healthcare organizations to navigate this complex landscape with confidence. Our expertise in custom software, AI-powered solutions, telemedicine platforms, and digital workflow automation ensures that your transformation is not only successful but sustainable.
The approach is simple yet powerful: start small, think big, and move fast. Launch targeted initiatives, measure outcomes, and scale strategically while keeping the patient experience at the center of every decision.
Sustainable digital transformation requires a vision for a fully integrated, patient-centric healthcare ecosystem. When technology, data, and care delivery are seamlessly connected, organizations can achieve predictive, personalized, and efficient healthcare at scale.
Collaboration and partnerships are critical to this journey; no single provider, system, or technology can achieve digital transformation alone. By working with experts, leveraging proven frameworks, and embracing innovation, healthcare leaders can drive meaningful change that benefits patients, providers, and the entire healthcare ecosystem.
The future is digital-first, and the time to act is now. Those who seize this opportunity will not only thrive in 2025 and beyond but also set a new standard for healthcare delivery in an increasingly connected world.
Key Takeaways

Digital transformation in healthcare is no longer optional; it’s essential for staying competitive and delivering patient-centered care.
Here’s what healthcare leaders should remember:
- Assess readiness and set priorities: Understand your organization’s current digital maturity and focus on technologies that deliver the most immediate value.
- Embrace the three pillars: Healthcare software, mobile apps, and AI solutions are the core drivers of operational efficiency, patient engagement, and better outcomes.
- Start small, scale smart: Pilot initiatives, measure results, and expand strategically to achieve sustainable transformation.
- Keep patients at the center: Every technology investment should enhance the patient experience, improve access, and personalize care.
- Collaborate and partner: Leverage expertise from technology providers, consultants, and cross-industry partners to accelerate your digital journey.
By focusing on these priorities, healthcare organizations can turn digital transformation from a buzzword into a measurable advantage for patients, providers, and the entire ecosystem. By leveraging innovative tools, software, and AI solutions, they can improve patient care, streamline operations, and stay ahead in a rapidly evolving landscape.
Partner with Bitcot to turn your vision into reality.
Our healthcare software development services help hospitals, clinics, and health-tech startups build custom, AI-powered solutions tailored to your unique needs. From EMR/EHR integration and telemedicine platforms to mobile apps and workflow automation, we provide end-to-end support for your digital transformation journey.
Start small, think big, and move fast; let Bitcot guide you every step of the way toward a more efficient, patient-centric, and digitally empowered healthcare ecosystem.
Get in touch with our team.